Although attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has often been viewed as a childhood disorder, the prevalence of ADHD in adults is estimated to be 4.4% based on recent epidemiologic data.1 ADHD that persists into adolescence and adulthood is associated with significant impairment in multiple domains of life, including academic and occupational performance, interpersonal relationships, driving, and financial and legal issues. Yet, this disabling disorder is frequently missed by clinicians. This article provides guidance for clinicians on how to recognize and assess ADHD in adolescents and adults and on the use of screening tools and rating scales. It also presents an overview of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatment strategies and discusses how to design treatment regimens targeted to the specific patient’s pattern of impairment.
DOMAINS OF LIFE AFFECTED IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS
Gregory W. Mattingly, MD, described how the core symptoms of ADHD—problems with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity—present across different phases of life.
Prevalence
ADHD is a chronic and pervasive neurobiological disorder. Until recently, it was generally viewed as a childhood disorder that did not continue into adolescence or adulthood. However, based on data from the National Comorbidity Replication Survey (NCS-R), Kessler et al1 estimated the prevalence of ADHD in adults to be 4.4%. In a group of children with ADHD followed from 7 years of age to adulthood, Barkley et al2 found that approximately 80% still had impairment due to ADHD symptoms as adolescents and two-thirds had such impairment as adults.
Neurobiological Findings
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies have shown a delay of more than 2 years in cortical maturation in children with ADHD, especially in prefrontal regions controlling cognition and impulsive emotions,3 with functional neurologic problems that make it more difficult to focus and stay on track persisting in the brains of adults with ADHD.4
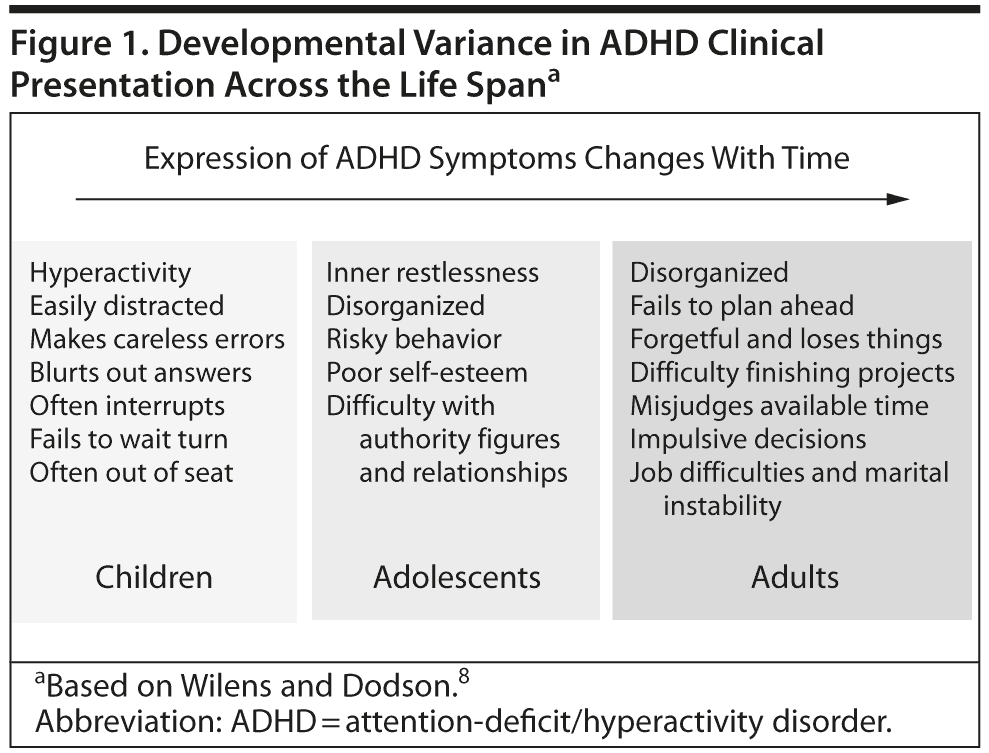
Clinical Presentations Across the Life Span
There are 3 ADHD subtypes: combined (most common in all age groups), primarily inattentive, and primarily hyperactive-impulsive. Hyperactive-impulsive symptoms tend to diminish with age (Figure 1), which often leads to the misconception that the condition is improving. Thus, treatment rates decline dramatically from age 13 on, with many adolescents and young adults no longer receiving appropriate care.5 Childhood ADHD is more common in males than females (2:1 to 4:1).6 However, the rate is closer to 1:1 in adults because girls have higher rates of the inattentive subtype, which is more likely to persist into adulthood, often unrecognized due to the absence of overt hyperactivity.7
The fidgety, restless boy who could not sit still in elementary school no longer runs around the room in high school, but tends to be easily bored and distracted and may shut down and fall asleep at his desk or impulsively blurt things out, have relationship problems with parents and peers, and have trouble focusing and controlling impulses while driving. Because his cognitive struggles and subsequent frustration are likely to be missed, such a teenager is often thought of as “not trying” or as a “troublemaker.” Off at college and lacking external family support, he may have trouble getting up to go to class, staying focused in lectures, keeping up with assignments, and dealing with social issues such as dating and decisions about drug or alcohol use. Adults with ADHD may continue to have serious difficulties with attention and staying focused; with organizing, prioritizing, and planning; and perhaps with modulating impulsive emotions.8
Outcomes
Compared with age-matched controls, adolescents and adults with ADHD show serious impairment in multiple domains (90% in home lives, 89% in work lives, and 77% in social lives).2
Education/academic performance. Students with ADHD are significantly more likely to drop out of high school (17% vs 7%) and less likely to obtain a college degree (19% vs 26%).2,9-11
Occupational performance. Adults with ADHD are more likely to have been fired from a job, to have had multiple jobs, to be reprimanded or written up, to have shown up late for work over the previous 10 years, and to be currently unemployed than those without ADHD.2,9-11 One study9 found that 39% of those with ADHD earned less than $25,000 a year compared with 20% of those without ADHD. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates ADHD as one of the top 10 causes of missed work and reduced work efficiency in the world.12
Personal relationships. Adolescents and adults with ADHD have higher rates of emotional and interpersonal difficulties and problems with sexual impulsivity than those without ADHD. Only 47% of subjects with ADHD felt that they had a good relationship with their parents, and only 40% said they fit in well with their peers, compared with 70% of those without ADHD for both items.9 By 21 years of age, they tended to have had more sexual partners (19 vs 7), had higher rates of sexually transmitted diseases (17% vs 4%), and had a 37 times higher risk of a teenage pregnancy than those without ADHD.10 Similarly, adults with ADHD were found to have 3 times the number of sexual partners2,10 and be twice as likely to be divorced (28% vs 15%) as age-matched controls.9
Financial problems. Financial impulsivity (impulsive buying, excessive credit card debt) is a serious problem for adults with ADHD, 71% of whom say they have not saved for retirement.11
Traffic violations and accidents. Drivers with ADHD have higher rates of motor vehicle accidents, traffic and speeding violations, drunk driving, and license suspensions than those without ADHD.13 Motor vehicle accidents are a serious cause of morbidity and mortality in adults with ADHD, 26% of whom report 3 or more motor vehicle accidents in their lives compared with 9% of US adults.2,10
Legal problems. Untreated adolescents and adults with ADHD are twice as likely to have been arrested as those without ADHD.9
Comorbidity. Adults with ADHD have significantly higher rates of comorbid illness than those without ADHD. These include depression and anxiety, especially social anxiety (29%), and intermittent explosive disorder (19.6%).9 Untreated young adults with ADHD have significantly higher rates of nicotine, alcohol, and substance dependence and lower rates of successful smoking cessation than those without ADHD.9
ASSESSING PATIENT NEEDS AND FORMULATING TREATMENT GOALS
Lenard A. Adler, MD, discussed diagnostic criteria for ADHD, formulation of treatment goals, and tools for assessing ADHD.
Diagnostic Criteria
An individual must meet 4 major DSM-IV-TR criteria to be diagnosed with adult ADHD: (1) presence of significant inattentive and/or hyperactive/impulsive symptoms for at least 6 months; (2) childhood onset of significant symptoms before 7 years of age; (3) impairment due to symptoms in more than one setting (eg, school, work, social settings, home); and (4) other causes of symptoms ruled out.14
Treatment Targets
The goal of treatment is to lessen impairment from core symptoms. It is important to assess for academic or occupational problems related to inattention, social difficulties, and comorbid Axis I and II disorders.
Rating Scales
Rating scales, completed either by clinicians or by patients or significant others, can help diagnose adult ADHD and assess frequency and severity of symptoms. Although a number of well-validated scales are used in children, most are not very appropriate for adults because the items reflect symptoms relevant for children and younger adolescents.
A number of instruments have been developed for diagnosing adults. These include the Conners’ Adult ADHD Diagnostic Interview for DSM-IV,15 Barkley Current Symptoms Scale,16 Brown ADD Diagnostic Form,17 Kiddie SADS Diagnostic Interview ADHD Module,18,19 and Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale version 1.2.6
Symptom assessment scales for adults include the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS version 1.1) Symptom Checklist,20 a frequency-based 18-item symptom checklist developed by the WHO; Brown ADD Scale21; Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scales22; Wender-Reimherr Adult Attention Deficit Disorder Scale[1]; Barkley Adult ADHD Rating Scale23; Barkley’s Current Symptoms Scale16; and Adult Investigator Symptom Report Scale.[2]
Screening for ADHD in Clinical Settings
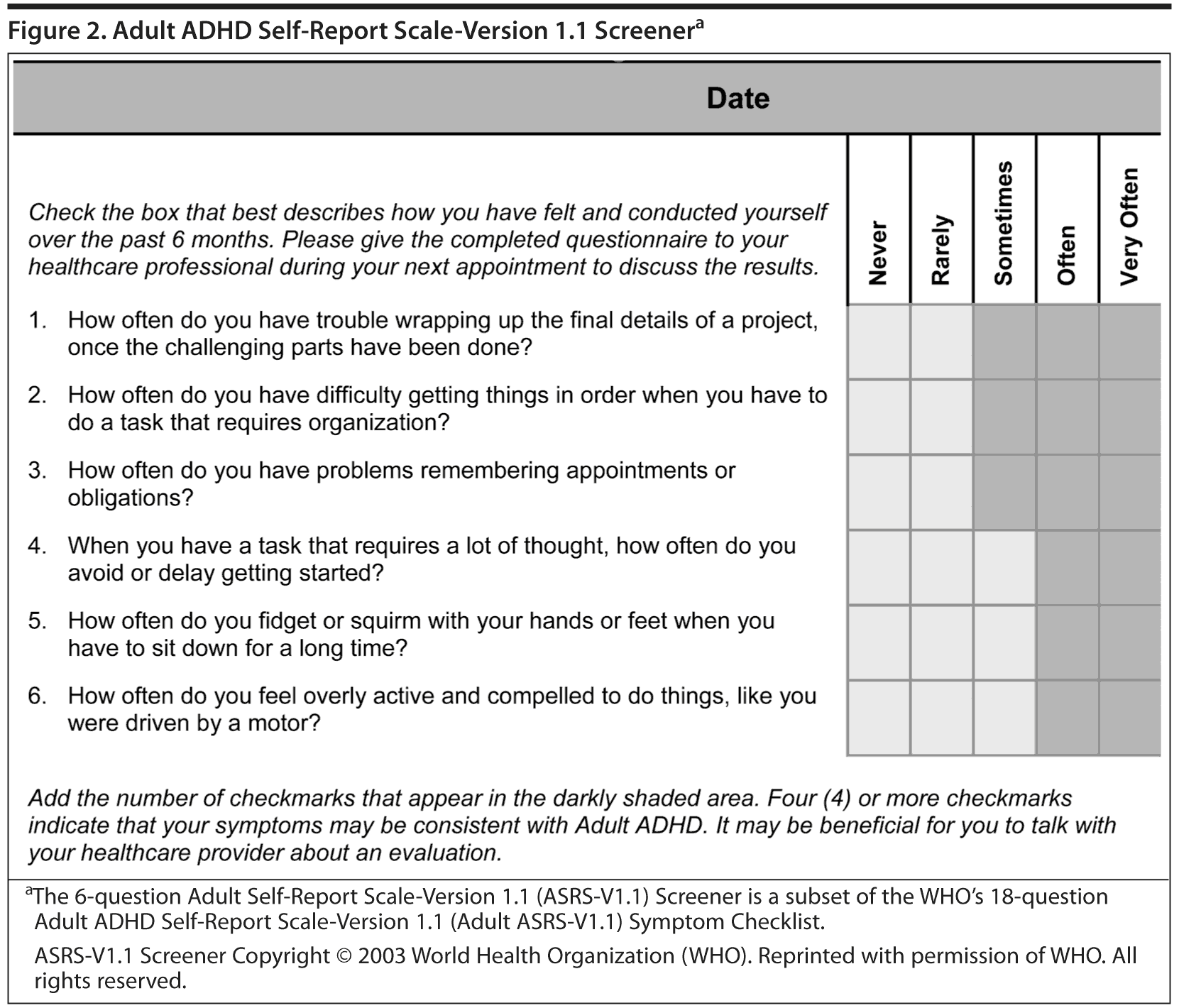
In assessing for ADHD, clinicians should look for real-world manifestations of symptoms in multiple settings. A 6-item subset of the ASRS version 1.1 has been developed for use as a screener (Figure 2), with 4 items assessing attention and 2 assessing hyperactivity/impulsivity, selected based on psychometric factor analyses of NCS-R data.20 A positive result on the screener indicates the need for more detailed evaluation.
RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT IN PRIMARY CARE
C. Brendan Montano, MD, discussed recognition and assessment of adult ADHD in primary care settings.
Underdiagnosis and Undertreatment
Although ADHD is one of the most common psychiatric disorders in primary care, the diagnosis is often missed in adults due to lack of disease awareness and failure of physician education. Frequently associated comorbid psychiatric conditions (major depression, generalized anxiety disorder, substance use disorders [SUDs]) also tend to mask or overlap many ADHD symptoms, further confounding the diagnosis. Many adult ADHD patients also tend to underreport their symptoms.24,25 A survey of 400 primary care practitioners (PCPs) who treated at least 30 patients per week who had psychiatric disorders found that nearly half felt uncomfortable diagnosing adult ADHD and that 65% referred adults with ADHD to specialists, mostly psychiatrists, for diagnosis, compared with 2% who referred those with depressive symptoms and 3% who referred those with anxiety symptoms.26
Recognition of ADHD
Both nature and nurture contribute to the etiology of ADHD, with genetic heritability (65%-75%) the largest contributor.27 Family physicians often identify ADHD in family members of already diagnosed patients (especially child/parent cohorts), an option not usually available to internists and subspecialists who treat only adults. It is estimated that environmental factors and central nervous system insults may account for ADHD in up to 35% of patients (eg, prenatal and perinatal factors including smoking and/or alcohol abuse in pregnancy, prematurity, high phenylalanine levels, birth asphyxia/anoxia, traumatic brain hemorrhage, and lead poisoning).28 Other factors yet to be identified may also contribute to the development of ADHD.
Adult patients with ADHD most commonly present in primary care settings either (1) through self-referral (especially if their child or another family member has been diagnosed with ADHD) or (2) with comorbid anxiety and depression, often associated with SUDs. Impulsivity, especially difficulty controlling anger, with subsequent relationship and legal problems and job loss also often leads patients to seek treatment.24
Thus, nearly half the time patients present with a comorbid condition (eg, depression, anxiety, SUDs)10 and often with chaotic life problems and are not aware that ADHD may be driving their comorbidity. One study29 found that 87% of adults with ADHD had at least 1 and 56% had at least 2 comorbid psychiatric disorders. Unfortunately, ADHD frequently persists after comorbid conditions have been treated and may result in only a partial response to treatment for major depression or another psychiatric disorder, increasing the risk of relapse or recurrence.30-32 When a patient appears to have a treatment-resistant depressive or anxiety disorder, with or without persistent difficulty with drug or alcohol abuse or addiction, screening for and treating underlying ADHD may help prevent relapse or recurrence of the comorbid condition(s).
Screening for ADHD
PCPs should rely on a clinical assessment of the patient’s current symptoms. The history of impairment must be longitudinal, since childhood, and not episodic, with significant and pervasive impairment in more than 1 realm of life (eg, school/work/social). Always inquire about a family history of ADHD and interview a family member if possible.6,33
The following questions are helpful as an initial screen for ADHD.
- Were you ever diagnosed with ADHD as a child?
- Do any first-degree members of your family have ADHD?
- Do you have a lifelong history of chronic distractibility, inattention, and/or disorganization?
If the answer to any of these questions is yes, the PCP can administer a screener such as the WHO 6-question screener (Figure 2). However, this screener is not diagnostic. If it is positive, a more comprehensive scale such as the 18-item self-report ASRS version 1.1 should be given to adolescents and adults to delineate and quantify ADHD symptoms and establish a baseline for measurement of treatment response.6,20 As discussed by Dr Mattingly, symptoms of inattention tend to persist in adults with ADHD, while hyperactivity is likely to morph into inner restlessness and may manifest as being a workaholic, choosing a very active job, and talking excessively, as well as exhibiting poor time management, procrastination, poor concentration, and difficulty completing tasks. Impulsive symptoms in adults may manifest as difficulty waiting in line; interrupting others; driving too fast, often with high rates of motor vehicle accidents; excessive use of nicotine, caffeine, or alcohol; irritability; impetuousness; impatience; quickness to anger; and impulsive changes in jobs and relationships, with frequent legal problems related to impulsive behavior.26,34
Be alert for chronicity, pervasiveness, and impairment associated with symptoms to establish the diagnosis. It is also important to rule out conditions that can affect cognition, such as metabolic illnesses (eg, vitamin B12 deficiency), thyroid illness, sleep apnea, dementia, fibromyalgia, traumatic brain injury, and environmental toxins.34 Adult patients with a constellation of impairing ADHD symptoms whose presentations do not meet full DSM-IV-TR criteria may be diagnosed with ADHD not otherwise specified or ADHD in partial remission.
When to Refer for Specialized Care
Patients with complicated presentations may need to be referred for specialized psychiatric care33; any patient with suicidal ideation or intent should be referred immediately. Other situations in which such a referral is often needed are diagnostic or therapeutic uncertainty, complicated psychiatric comorbidity, and symptoms that do not respond to approved medications. Clinicians may also want to consider a referral for specialized care for treatment reinforcement or cognitive-behavioral therapy or other psychosocial interventions to help patients get their lives in order.
CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
Jeffrey H. Newcorn, MD, discussed treatment options for adolescent and adult ADHD.
Nonpharmacologic Treatment
Psychosocial treatments can play an important role in treating ADHD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy can reduce severity of and impairment associated with ADHD symptoms as well as depression and anxiety.35,36 Also helpful are environmental modifications,10 including avoiding distracting surroundings, establishing centers for tasks (eg, paying bills), and structuring time (eg, using electronic calendars or day planners).
Pharmacologic Treatment: An Overview
Psychopharmacologic treatment for ADHD may utilize stimulant and/or nonstimulant medications. All of the major medication classes (ie, methylphenidate, amphetamine, and noradrenergic reuptake inhibitors) approved in children (although not every formulation in each class) are also approved in adults. Two α2 agonists, guanfacine and clonidine, are also approved for use in children but not in adults.
Duration of medication effect. For adults with ADHD, adequate dosing is needed to achieve effects that last through the day and into the evening, when they often must handle family responsibilities. Other impairments (eg, high incidence of motor vehicle accidents) also highlight the importance of adequate duration of treatment effects.
Stimulants
The following extended-release (XR) stimulant medications are approved for treatment of adult ADHD.
- Osmotic, controlled-release oral system (OROS) methylphenidate, a continuous-release formulation
- Dexmethylphenidate XR
- Mixed amphetamine salts XR
- Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (prodrug that is inactive until split into its component parts—inactive l-lysine and active dextroamphetamine)
Shorter acting preparations are approved for use in children but not adults.
Functional MRI studies have shown that stimulant medications increase neural activity in prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate, and basal ganglia, which is presumed to reflect their mechanisms of action.37 The mechanisms of action of methylphenidate and amphetamine are similar but not identical: both block reuptake to presynaptic dopamine and norepinephrine transporters, while amphetamine is also involved in release of catecholamine from presynaptic nerve terminals.38
Efficacy. All of the stimulant medications approved for adults have been shown to have comparable effects on cognition and inhibitory control when dosed comparably.39-41 The XR formulations have been found to maintain their effects into the evening, but duration of action varies considerably across individuals.39,41
Dosing. It is generally best to start with the lowest possible dose and titrate up based on side effects and response. While needing higher absolute doses, adolescents and adults may not require as high a relative dose (mg/kg dosing) as children to achieve the same effect.
Abuse potential. Although all of the stimulant medications are schedule II compounds and have abuse liability, OROS methylphenidate and lisdexamfetamine may have lower abuse liability.42,43 Variable findings exist concerning the effect of stimulant treatment on later risk for SUDs, with different studies finding increased, decreased, and no change in risk of later SUDs, although the majority suggest no increased risk and, in some cases, a decreased risk.44
Safety considerations. Stimulants are associated with some risk of cardiovascular adverse events because they cause small increases in pulse and blood pressure. Before beginning treatment, it is important to take a careful personal/family history to screen for congenital or acquired cardiac disease (eg, premature cardiac disease, syncope, heart murmur, palpitations, chest pain, postexercise symptoms, family history of early or sudden cardiac death) and determine need for a screening electrocardiogram.45 A routine medical examination is usually suggested (which often includes an electrocardiogram in adults). Also ask the patient about use of other medications, including over-the-counter agents, that might interact with stimulants. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and regularly during treatment.26
Side effects. The most common side effects of stimulants are dry mouth, insomnia, nausea or abdominal pain, appetite suppression, headache, edginess, and slight changes in cardiovascular indices not considered clinically significant at the group level. Although these are generally regarded as “nuisance” effects, they can have a significant impact on adherence. The most important initial side effects are insomnia and appetite suppression, which patients usually (but not always) accommodate to over the course of treatment. Irritability and other mood-related adverse effects can be particularly problematic when present.
Nonstimulants
Stimulants are highly effective, but some patients do not respond well to, have difficulty tolerating, or are unwilling to take them. The mechanism of action of the nonstimulants is based on catecholamine neurotransmission (ie, direct effects on norepinephrine in numerous brain regions, direct/indirect effects on dopamine in prefrontal cortex).46 Nonstimulants have a smaller overall effect size than stimulants, but they may be highly effective for selected individuals, particularly patients with active SUDs or significant tics or anxiety. Nonstimulants can take several weeks to achieve full clinical effects, while stimulants have a more rapid onset of effect.26,47,48
Atomoxetine, a selective norepinephrine reuptake blocker, is the only nonstimulant approved for use in both adults and children.49 It has direct effects on dopamine in prefrontal cortex, where dopamine reuptake is achieved through norepinephrine transporters. It does not directly affect dopamine in the striatum and nucleus accumbens, where dopamine may produce reinforcement, consistent with its lack of abuse potential.44 Atomoxetine was not found to be reinforcing in animal self-administration studies, and human studies also suggest low abuse liability.50 Common side effects in adults include dry mouth; insomnia; initial nausea and decreased appetite, which generally resolve with treatment; decreased libido; and erectile difficulty in older males.49 Like the stimulants, atomoxetine can cause small increases in pulse and blood pressure, so clinicians should follow the same cardiovascular screening and monitoring procedures as for stimulants.49
Extended-duration formulations of the α2 agonists guanfacine and clonidine, both of which were originally approved for treatment of hypertension, are now approved for use in children and adolescents (but not adults) with ADHD. The α2 agonists bind to postsynaptic α2 receptors, which enhance neurotransmission in prefrontal cortex and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Because these agents tend to lower pulse and blood pressure, they may be good options for adults with certain cardiovascular issues. However, these medications have not been substantively studied in adults.51
Agents That Have Not Been Approved
Although not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for ADHD, bupropion, an approved antidepressant,52 has been found effective in adult ADHD. There are positive findings in studies using modafinil, an atypical stimulant approved for narcolepsy, in children with ADHD,53 but its utility in adults is uncertain. Tricyclic antidepressants are effective for ADHD, but because of cardiovascular toxicity and tolerability issues, they are generally no longer used.
Comorbid Conditions
Given the limited data on ADHD and comorbidity in adults, clinicians should extrapolate from child and adolescent findings. Consider potential drug interactions between agents used to treat ADHD and those used for comorbid conditions. Findings in children suggest that atomoxetine may be useful in treating ADHD with comorbid anxiety.54 Atomoxetine and the α2 agonists may also be helpful for ADHD with comorbid tic disorders or Tourette’s syndrome.55 Many individuals with comorbid tic disorders can also be treated with stimulants with careful monitoring, especially as intensity of tics tends to decrease with age. Bupropion may be a reasonable choice for adults with ADHD and significant depression.
SUMMARY
ADHD in adults can be treated effectively with both stimulant and nonstimulant medications. Treatment should fit the extent of impairment throughout the day, so that it is generally better to use a long-acting preparation for adults and adolescents to obtain treatment coverage throughout the day and into the evening. Longer acting preparations may also be less likely to be diverted for abuse. Cardiac monitoring before starting and during treatment is important. To manage comorbid conditions, clinicians can consider monotherapy with a medication that may be effective for both conditions or a combination of medications, with care taken to avoid drug interactions. Psychosocial interventions and/or environmental manipulation are often also required to achieve optimum outcomes.
Drug names: atomoxetine (Strattera), bupropion (Wellbutrin, Aplenzin, and others), clonidine (Catapres, Duraclon, and others), guanfacine (Intuniv, Tenex, and others), lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Focalin, Daytrana, and others), modafinil (Provigil).
REFERENCES
1. Kessler RC, Adler L, Barkley R, et al. The prevalence and correlates of adult ADHD in the United States: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(4):716-723. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.163.4.716
2. Barkley RA, Fischer M, Smallish L, et al. Young adult outcome of hyperactive children: adaptive functioning in major life activities. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006;45(2):192-202. PubMed doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000189134.97436.e2
3. Shaw P, Eckstrand K, Sharp W, et al. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is characterized by a delay in cortical maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(49):19649-19654. PubMed doi:10.1073/pnas.0707741104
4. Bush G, Spencer TJ, Holmes J, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of methylphenidate and placebo in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder during the multi-source interference task. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65(1):102-114. PubMed doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2007.16
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Increasing prevalence of parent-reported attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder among children—United States, 2003 and 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010;59(44):1439-1443. PubMed
6. Adler L, Cohen J. Diagnosis and evaluation of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2004;27(2):187-201. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.psc.2003.12.003
7. Kessler RC, Green JG, Adler LA, et al. Structure and diagnosis of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: analysis of expanded symptom criteria from the Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(11):1168-1178. PubMed doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.146
8. Wilens TE, Dodson W. A clinical perspective of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder into adulthood. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65(10):1301-1313. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.v65n1003
9. Biederman J, Faraone SV, Spencer TJ, et al. Functional impairments in adults with self-reports of diagnosed ADHD: a controlled study of 1001 adults in the community. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(4):524-540. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.v67n0403
10. Barkley RA. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2005.
11. Barkley RA, Murphy KR, Fischer M. ADHD in Adults: What the Science Says. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2007.
12. de Graaf R, Kessler RC, Fayyad J, et al. The prevalence and effects of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) on the performance of workers: results from the WHO World Mental Health Survey Initiative. Occup Environ Med. 2008;65(12):835-842. PubMed doi:10.1136/oem.2007.038448
13. Barkley RA, Murphy KR, Kwasnik D. Motor vehicle driving competencies and risks in teens and young adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics. 1996;98(6, pt 1):1089-1095. PubMed
14. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
15. Epstein J, Johnson DE, Conners CK. Conners’ Adult ADHD Diagnostic Interview for DSM-IV. North Tonawanda, NY: MHS Psychological Assessments and Services. http://downloads.mhs.com/caadid/caadid.pdf.
16. Barkley RA, Murphy KR. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Clinical Workbook. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Guilford; 2005.
17. Brown TE. Brown Attention Deficit Disorder Diagnostic Forms for Adolescents and Adults. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation; 2001. http://www.drthomasebrown.com/assess_tools/brown_forms.html.
18. Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, et al. Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Age Children-Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36(7):980-988. PubMed doi:10.1097/00004583-199707000-00021
19. Ambrosini PJ. Historical development and present status of the Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Age Children (K-SADS). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2000;39(1):49-58. PubMed doi:10.1097/00004583-200001000-00016
20. Kessler RC, Adler L, Ames M, et al. The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS): a short screening scale for use in the general population. Psychol Med. 2005;35(2):245-256. doi:10.1017/S0033291704002892www.hcp.med.harvard.edu/ncs/asrs.php PubMed
21. Brown TE. Brown Attention Deficit Disorder Scales for Adolescents and Adults (BADDS). San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation; 2001. http://www.drthomasebrown.com/assess_tools/index.html.
22. Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow E. Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scales (CAARS). North Tonawanda, NY: MHS Psychological Assessments and Services; 2004-2011. http://www.mhs.com/product.aspx?gr=cli&prod=caars&id=overview.
23. Barkley RA. Barkley Adult ADHD Rating Scale-IV (BAARS-IV). New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2011.
24. Faraone SV, Spencer TJ, Montano CB, et al. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: a survey of current practice in psychiatry and primary care. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(11):1221-1226. PubMed doi:10.1001/archinte.164.11.1221
25. Sandra Kooij JJ, Marije Boonstra A, Swinkels SH, et al. Reliability, validity, and utility of instruments for self-report and informant report concerning symptoms of ADHD in adult patients. J Atten Disord. 2008;11(4):445-458. PubMed doi:10.1177/1087054707299367
26. Adler L, Shaw D, Sitt D, et al. Issues in the diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD by primary care physicians. Prim Psychiatry. 2009;16(5):57-63.
27. Faraone SV, Doyle AE. The nature and heritability of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2001;10(2):299-316, viii-ix. PubMed
28. Faraone SV, Perlis RH, Doyle AE, et al. Molecular genetics of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57(11):1313-1323. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.024
29. McGough JJ, Smalley SL, McCracken JT, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: findings from multiplex families. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(9):1621-1627. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.9.1621
30. Alpert JE, Maddocks A, Nierenberg AA, et al. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in childhood among adults with major depression. Psychiatry Res. 1996;62(3):213-219. PubMed doi:10.1016/0165-1781(96)02912-5
31. Fones CS, Pollack MH, Susswein L, et al. History of childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) features among adults with panic disorder. J Affect Disord. 2000;58(2):99-106. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0165-0327(99)00065-8
32. Wilens TE. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the substance use disorders: the nature of the relationship, subtypes at risk, and treatment issues. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2004;27(2):283-301. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0193-953X(03)00113-8
33. Montano B. Diagnosis and treatment of ADHD in adults in primary care. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65(suppl 3):18-21. PubMed
34. Wilens TE, Biederman J, Faraone SV, et al. Presenting ADHD symptoms, subtypes, and comorbid disorders in clinically referred adults with ADHD. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(11):1557-1562. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.08m04785pur
35. Solanto MV, Marks DJ, Wasserstein J, et al. Efficacy of meta-cognitive therapy for adult ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2010;167(8):958-968. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09081123
36. Safren SA, Sprich S, Mimiaga MJ, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy vs relaxation with educational support for medication-treated adults with ADHD and persistent symptoms: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2010;304(8):875-880. PubMed doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1192
37. Vaidya CJ, Austin G, Kirkorian G, et al. Selective effects of methylphenidate in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a functional magnetic resonance study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(24):14494-14499. PubMed doi:10.1073/pnas.95.24.14494
38. Spencer T, Biederman J, Wilens T. Assessment and treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. In: Martin A, Scahill L, Charney D, et al, eds. Textbook of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2nd ed. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press; 2011:437-452.
39. Weisler RH, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, et al. Mixed amphetamine salts extended-release in the treatment of adult ADHD: a randomized, controlled trial. CNS Spectr. 2006;11(8):625-639. PubMed
40. Biederman J, Mick E, Surman C, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of OROS methylphenidate in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59(9):829-835. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.09.011
41. Wigal T, Brams M, Gasior M, et al; 316 Study Group. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study of the efficacy and safety of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: novel findings using a simulated adult workplace environment design. Behav Brain Funct. 2010;6(1):34. PubMed doi:10.1186/1744-9081-6-34
42. Spencer TJ, Biederman J, Ciccone PE, et al. PET study examining pharmacokinetics, detection and likeability, and dopamine transporter receptor occupancy of short- and long-acting oral methylphenidate. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(3):387-395. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.163.3.387
43. Jasinski DR, Krishnan S. Abuse liability and safety of oral lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in individuals with a history of stimulant abuse. J Psychopharmacol. 2009;23(4):419-427. PubMed doi:10.1177/0269881109103113
44. Wilens TE, Adler LA, Adams J, et al. Misuse and diversion of stimulants prescribed for ADHD: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;47(1):21-31. PubMed doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31815a56f1
45. American Academy of Pediatrics, American Heart Association. American Academy of Pediatrics/American Heart Association clarification of statement on cardiovascular evaluation and monitoring of children and adolescents with heart disease receiving medications for ADHD: May 16, 2008. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2008;29(4):335. PubMed doi:10.1097/DBP.0b013e31318185dc14
46. Bymaster FP, Katner JS, Nelson DL, et al. Atomoxetine increases extracellular levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rat: a potential mechanism for efficacy in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;27(5):699-711. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00346-9
47. Newcorn JH, Kratochvil CJ, Allen AJ, et al; Atomoxetine/Methylphenidate Comparative Study Group. Atomoxetine and osmotically released methylphenidate for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: acute comparison and differential response. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165(6):721-730. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.05091676
48. Pliszka S; AACAP Work Group on Quality Issues. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007;46(7):894-921. PubMed doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e318054e724
49. Michelson D, Adler L, Spencer T, et al. Atomoxetine in adults with ADHD: two randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53(2):112-120. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01671-2
50. Heil SH, Holmes HW, Bickel WK, et al. Comparison of the subjective, physiological, and psychomotor effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate in light drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2002;67(2):149-156. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(02)00053-4
51. Newcorn JH, Clerkin S, Schulz KP, et al. Adrenergic agonists: clonidine and guanfacine. In: Martin A, Scahill L, Charney D, et al, eds. Textbook of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2nd ed. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press; 2011:263-274.
52. Wilens TE, Spencer TJ, Biederman J, et al. A controlled clinical trial of bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(2):282-288. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.158.2.282
53. Biederman J, Swanson JM, Wigal SB, et al; Modafinil ADHD Study Group. A comparison of once-daily and divided doses of modafinil in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(5):727-735. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.v67n0506
54. Geller D, Donnelly C, Lopez F, et al. Atomoxetine treatment for pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with comorbid anxiety disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007;46(9):1119-1127. PubMed doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e3180ca8385
55. Spencer TJ, Sallee FR, Gilbert DL, et al. Atomoxetine treatment of ADHD in children with comorbid Tourette syndrome. J Atten Disord. 2008;11(4):470-481. PubMed doi:10.1177/1087054707306109
[1]*Available on request from Frederick W. Reimherr, MD, Mood Disorders Clinic, Department of Psychiatry, University of Utah Health Sciences Center, Salt Lake City, UT 84132.
[2]Available on request from Lenard A. Adler, MD, Adult ADHD Program, NYU School of Medicine ([email protected]).