ABSTRACT
The half-life of a drug is most commonly defined as the time taken for the plasma or blood level of the drug to fall by half. Elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life, and biologic half-life are interchangeably used most commonly to describe the half-life of drugs that follow first-order or linear pharmacokinetics; that is, in single-compartment models, where the fall in blood level is proportionate to the concentration of the drug in blood. In 2 compartment models, where the drug equilibrates between blood and (for example) adipose tissue, during elimination there is a sharp initial fall in blood levels followed by a gradual subsequent fall; when drugs display this biphasic elimination pattern, the half-life corresponding to the second phase is what is clinically relevant, and this half-life is known as the terminal half-life. Half-life is influenced by drug distribution, drug metabolism, and drug excretion, each of which can be influenced by many factors such as age, use of concurrent medications, and presence of liver or renal disease. In order to maintain uniform blood levels and reduce the adverse effect risk, drugs with short half-lives need to be dosed more frequently. Drugs with short half-lives are more likely to be associated with withdrawal or discontinuation syndromes. The duration of action of a drug, time to steady state levels, and time to washout are each influenced by the value of the drug half-life. All these terms and concepts are defined and explained with the help of clinically relevant examples. Mental health care professionals who prescribe to patients need to know the half-lives of the drugs that they prescribe, the half-lives of active metabolites, if any, how these half-lives may differ with individual patient characteristics, and how to use this knowledge to prescribe to best advantage.
J Clin Psychiatry 2022;83(4):22f14584
To cite: Andrade C. The practical importance of half-life in psychopharmacology. J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4):22f14584.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.22f14584
© 2022 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
The half-life of a drug, represented by the symbol T/2, is defined in different ways. It is the time taken for half of the administered dose of a drug to be eliminated from the body; or, the time taken for half the quantity of the drug in the body to be eliminated from the body; or, the time taken for the plasma or blood level of the drug to drop by half.1,2 Each of these definitions carries a different meaning, and what the half-life of a drug is found to be can also vary or appear to vary depending on contexts such as formulation, route of administration, and individual variations in drug distribution, metabolism, and excretion, among other factors. This article limits itself to an explanation of clinically relevant concepts related to half-life and practical issues related to half-life.
Terms and Concepts
Pharmacology textbooks are packed with terms and concepts related to the subject of drug distribution, clearance, and half-life, none of which is straightforward and all of which are related through formidable formulae. To complicate matters, some terms are inconsistently used. This article will therefore explain only what is actually necessary for a practicing clinician to know.
Elimination half-life. Elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life, and biologic half-life are commonly used interchangeably and refer to the time taken for the blood level of a drug to fall by 50%.1 As a brief aside, the term blood level is used nonspecifically, here; whether blood, plasma, or serum is used as the reference fluid depends on the drug and on the method of assay. It is seldom necessary for clinicians to know and specify what the reference fluid is when “levels” are ordered.
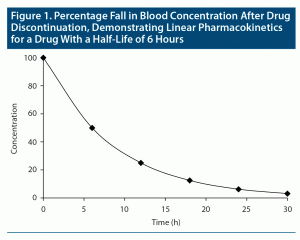
The concept of elimination half-life is easy to understand when drugs follow “first-order kinetics”; that is, when pharmacokinetics are “linear.” In this situation, when the drug is eliminated (ie, metabolized and excreted from the body), the fall in blood level is proportionate to the concentration of the drug in blood. So, in a graph, when drug concentration is plotted on the Y-axis against time on the X-axis, provided that there is no readministration of the drug, the fall in drug concentration will be depicted by a smoothly curved line (Figure 1). First-order kinetics are seen in “single-compartment models”; that is, when the drug is distributed only in the primary compartment, blood.
Lamotrigine, with a half-life of 23–37 hours, and desvenlafaxine, with a half-life of about 10 hours, are examples of drugs that show linear pharmacokinetics.3,4
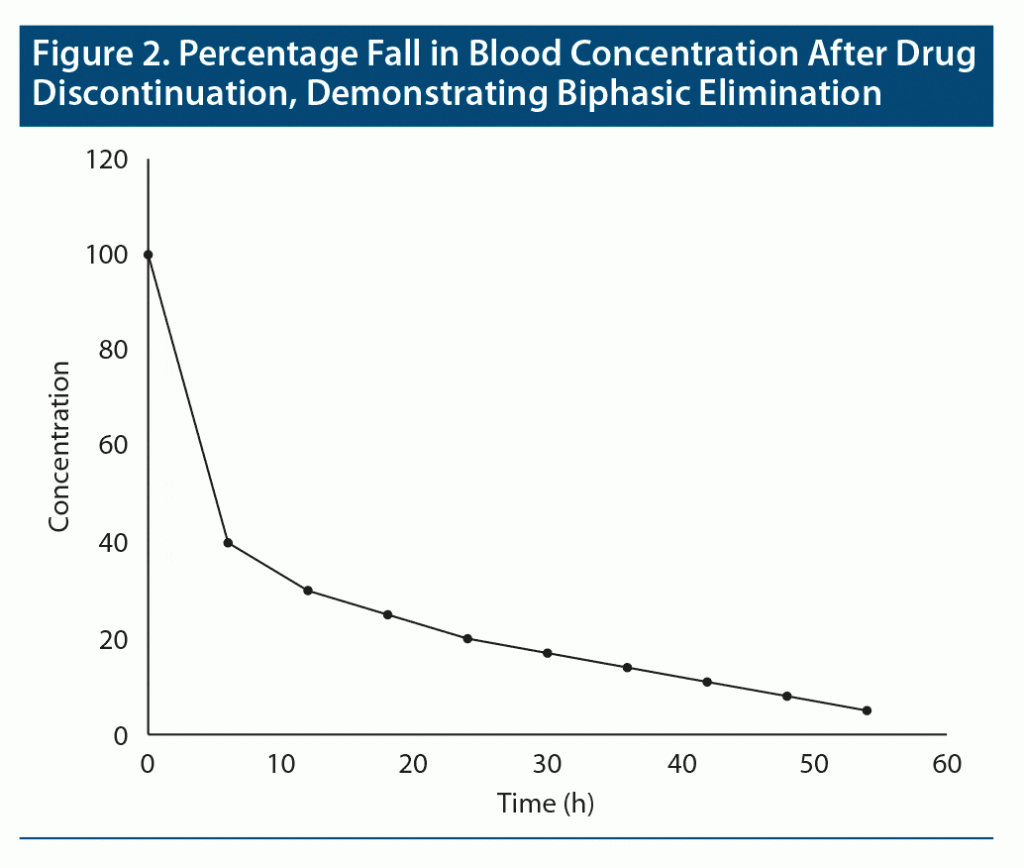
Terminal half-life. What happens when drugs are distributed into more than one compartment, as in the case of drugs that are highly lipid soluble? Consider diazepam as an example.1 When diazepam is administered, after absorption it rapidly diffuses from blood into lipid reservoirs; the greater the adiposity of the individual, the greater this diffusion. So, soon after administration, the blood level of diazepam rapidly falls until equilibrium is reached between blood and lipid compartments. As the diazepam fraction that is in blood is gradually metabolized, re-equilibration between lipid and blood compartments occurs to compensate for the metabolized moiety. This results in a more gradual fall in blood levels. Thus, diazepam displays biphasic decline in blood levels: there is a rapid initial decline followed by a subsequent slow decline. Biphasic elimination for a hypothetical drug is shown in Figure 2.
Only the second phase in biphasic elimination is relevant to pharmacologic action. This is because the fraction of a drug that is in blood is what is distributed to the target tissue, and hence what determines the clinical action of the drug.
The half-life of the drug that corresponds to the second phase of decline is known as the terminal half-life.2 This is the half-life that is usually reported for drugs with biphasic elimination.
Factors That Influence Half-Life
Whatever influences the distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a drug can increase its half-life. With regard to distribution, for drugs such as diazepam1 and penfluridol5 that are substantially distributed into adipose tissue, greater adiposity is associated with greater storage of the drug in lipid reservoirs, and hence greater availability of the drug for return to blood as blood levels fall due to metabolism. The net result is a longer half-life. Elderly persons tend to have a higher adipose to muscle tissue ratio, and this is therefore one reason why the half-life of some drugs, such as diazepam, is greater in the elderly.6
With regard to metabolism, individuals inherit different metabolic predispositions. As an example, most people (67%–90%) are cytochrome P450 (CYP)2D6 rapid (extensive) metabolizers; the rest, depending on ethnicity, are slow, intermediate, or ultrarapid metabolizers.7 So, the half-life of a drug that is metabolized by CYP2D6 would depend on the metabolic status of the individual. Risperidone and venlafaxine are examples of drugs that are metabolized by CYP2D6.8,9
With regard to excretion, half-life is not affected by renal disease for drugs that are metabolized by the liver. However, for drugs such as lithium, milnacipran, pregabalin, and gabapentin that are not metabolized or little metabolized, and that are eliminated by renal excretion,10 half-life increases in proportion to the severity of the renal disease.
Age, sex, nutritional status, adiposity, dietary preferences, habits such as smoking, use of concurrent medications, physiologic states such as pregnancy, pathologic states such as liver disease, and others can affect one or more of the 3 processes listed above, thereby influencing the half-life of psychotropic and other drugs. Clinicians therefore need to know not only the half-life of the drug that they are prescribing but also what the half-life might be given the presence of one or more of these factors in the patient to whom the drug is being prescribed.
When Is Half-Life Assessed?
Half-life can be assessed after single dosing. This is often done in phase 1 clinical trials during new drug development. However, the information from such studies is hardly of interest because few drugs in psychiatry are administered in one-off situations; ketamine, in the context of depression, is one such drug.11
Half-life is more usually assessed after steady state has been attained. Assessment of terminal half-life, in particular, tends to be more accurate at steady state. Finally, in the case of drugs that induce (eg, carbamazepine) or inhibit (eg, fluoxetine) their own metabolism,12,13 it is necessary to know what the half-life is at least 2–4 weeks after treatment initiation, when enzyme induction or inhibition reaches its peak. In the case of carbamazepine, for example, the half-life is 18–65 hours after a single dose and 10–20 hours after multiple doses.12
Half-Life, Duration of Action, and Dosing
Drugs that have a short half-life stay in the body for a shorter period and so have a shorter duration of action. Such drugs therefore need to be administered at more frequent dosing intervals. As an example, the half-life of carbamazepine is 10–15 hours during maintenance therapy.14 So, when carbamazepine is used in the long-term treatment of patients with partial seizures, it is dosed twice or even thrice a day in order to maintain the uniform blood levels, across the course of the day, that are necessary to reduce the risk of breakthrough seizures.
Drugs that have a long half-life stay longer in the body and so have a longer duration of action. Such drugs can conveniently be dosed once a day or even less frequently. As an example, paliperidone has a half-life of about 24 hours15 and can be administered in a once-daily dosing schedule. Memantine has a half-life of about 70 hours and is somewhat illogically recommended in a twice-daily dosing schedule16; once-daily dosing with memantine has been found safe and effective in Alzheimer patients.17
Most psychopharmacologic treatments, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics, have a half-life of a day or longer, which is why once-daily dosing is usual in psychiatry. However, there are certain circumstances when, despite long half-life, divided dosing may be recommended. As an example, if a drug such as lithium is associated with adverse effects when administered in a single dose, divided doses may be better tolerated.18 Or, if there is need for daytime sedation in a severely disturbed psychotic inpatient, twice daily dosing with a sedating antipsychotic may be recommended. Or, during early pregnancy, if there are concerns about fetal risks associated with peak blood levels following each once-daily dose of a psychotropic drug, twice- or thrice-daily dosing may be suggested; the lower peaks associated with the lower (split) doses may be less likely to be associated with fetal risks. Some of these practices are backed more by experience or tradition than by evidence.
Sedating psychotropics are best administered in a single dose at night. However, if the administered drug has a long half-life, blood levels may still be high when the patient awakes in the morning. The patient will then experience a “hangover” characterized by grogginess, slowed thinking, and slowed reflexes. This may happen, for example, with olanzapine, which has a half-life of 21–54 hours.19 Because lowering the dose of olanzapine may not be an option for most patients, a practical strategy that could reduce the hangover risk is to dose olanzapine a few hours before bedtime; that is, either late in the evening or with the nighttime meal; food does not interfere with the absorption of olanzapine.20 Olanzapine is absorbed slowly; it takes 5–8 hours for peak blood levels to be attained.21 So, with late evening dosing, blood olanzapine levels would be sufficiently high at the time of retiring to bed to coincide with the scheduled sleep time. And, by the time the patient awakes in the morning, the blood levels could be expected to have fallen more than they would have had the patient taken the drug at bedtime. The risk of hangover is thus reduced in proportion to the lower blood levels at the time of awaking.
Clomipramine has a half-life of about 24 hours.22 Clomipramine treatment may also be associated with a morning hangover. The use of sustained-release clomipramine23 would result in the same dose being absorbed across a longer period; the peak blood levels would hence be substantially lower, by about half.24 In consequence, the risk of adverse effects associated with high blood levels, including the risk of hangover, would be lower. So, artificially prolonging half-life through the use of a sustained-release formulation is another strategy to reduce drug adverse effects.25
Half-Life and Active Metabolites
Knowledge about the half-life of a drug is incomplete when the drug has active metabolites that prolong the action of the parent drug. When drugs have active metabolites, it is necessary to know not just the half-life of the parent drug but the half-life of the active metabolites, as well; in this context, how potent the active metabolite is with regard to the parent drug is also a matter of importance. Psychotropic drugs with active metabolites include anxiolytics such as diazepam and clobazam, antidepressants such as fluoxetine and venlafaxine, and antipsychotics such as risperidone and cariprazine. For two of these drugs, risperidone and venlafaxine, the active metabolites (paliperidone and desvenlafaxine, respectively) were marketed as drugs in their own right several years after the parent drugs were marketed.
Half-Life and Extended Duration of Action
Drugs may have a longer duration of action than predicted by their half-lives if their action is irreversible. As an example, the classical monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), such as tranylcypromine, irreversibly inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO); therefore, MAO-driven metabolism of substances such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and tyramine normalizes only after new MAO is synthesized, and this process takes about 2 weeks to be complete after the MAOI has been washed out of the body. This is why it is recommended that monoamine reuptake inhibitor antidepressants, such as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, be started only after at least 2 weeks have elapsed following washout of previous MAOI therapy.26,27
Special Drug Formulations and Half-Life
If half-life is defined as the time taken for half of the administered dose of a drug to be eliminated from the body, then the time for absorption can become a factor when the route of administration is oral. So, when single dose pharmacokinetics are studied, the half-life of a drug is ideally determined after intravenous (iv) administration of the drug. After iv administration, the entire dose of the drug is immediately available for metabolism and excretion; in contrast, when a drug is orally administered, the value of the half-life will be increased in proportion to the delay in the absorption of the drug. This is the reason why drugs that are orally administered as sustained-release, extended-release, or other time-release formulations have an artificially lengthened half-life.25 For the same reason, whereas the half-life of an antipsychotic remains the same, regardless of formulation, artificial prolongation can be achieved with long-acting injections.28
Half-Life and Steady State
If the dose of a drug that is administered is greater than the dose that is eliminated during the dosing interval, it will take about 5 half-lives for a drug to reach steady state levels; why this is so is explained in the next section. Steady state is attained when the quantity of drug ingested per day is the same as the quantity of drug eliminated per day. Here, “day” as the unit of time is not set in stone; other units of time may also apply, as in the case of drugs that are administered once in 6 hours (eg, some antibiotics) or once a week (eg, penfluridol). Steady state levels are higher or lower when drugs are more frequently or less frequently administered.
Steady state is important because this is when blood levels are reasonably stable across the course of the dosing interval. So, if blood levels are ordered, they are ordered only after steady state has been achieved. Of note, whereas drug adverse effects may emerge early because of the sudden exposure of the body to a new substance, adverse effects tend to be clearly present only when a critical threshold, usually related to blood level, is reached. The highest stable blood levels are reached at steady state.
As a brief aside, readers may note that blood levels are not uniformly level at steady state. They transiently peak as the drug is absorbed after each dosing occasion and gradually fall thereafter, reaching a trough just before the next dosing occasion. Peaks and troughs at steady state are not far apart, in units of concentration, which is why the term steady state is used. For a fixed value of dose per day, the narrower the dosing interval with divided dosing the narrower the gap in blood levels between peak and trough. So, if carbamazepine is administered in a dose of 600 mg/d, the gap between peaks and troughs will be narrower if the drug is dosed at 200 mg thrice a day than if it administered as a single dose at night. Thus, more frequent dosing is associated with less fluctuation in steady state levels.
Whereas peaks in steady state levels may be associated with drug adverse effects, troughs may be associated with loss of efficacy. This is why anticonvulsant levels are assessed during troughs; blood for testing is drawn just before the next dosing occasion.
Half-Life and Washout
Consider a drug that displays linear or first-order pharmacokinetics; that is, blood levels increase in proportion to the dose and decrease in proportion to the concentration. Returning to the definition of half-life as the time required for the blood level to drop by half, if the steady state blood level of a drug with linear pharmacokinetics is considered to be 100%, then, if the drug is suddenly withdrawn, its level will drop to 50% after the first half-life, to 25% after the second half-life, to 12.5% after the third half-life, to 6.25% after the fourth half-life, and to 3.125% after the fifth half-life (Figure 1). In other words, after 5 half-lives, a drug is for all practical purposes washed out of the body. By reverse logic, it takes 5 half-lives for a drug to reach steady state.
From the above, it is clear that drugs with short half-lives reach steady state quicker and are washed out sooner, and drugs with long half-lives reach steady state more slowly and take longer to wash out. Reaching steady state sooner has the potential benefit of reaching therapeutic levels more quickly, and reaching washout sooner has the potential benefit of getting rid of adverse effects more quickly. With most drugs in psychiatry, though, short half-lives do not necessarily translate into earlier benefits, and where higher levels need to be attained sooner than can be attained by waiting for 5 half-lives, this is achieved by administering higher initial (loading) doses, or by crowding earlier doses and then spacing them out into the recommended dosing intervals. Such a strategy is followed, for example, with the long-acting antipsychotic injection paliperidone palmitate.29
A short half-life is often problematic with neuropsychiatric medications because rapid washout can be associated with drug withdrawal symptoms as with benzodiazepines or with drug discontinuation syndromes as with antidepressants. This is why, for example, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam are more difficult to discontinue than long-acting benzodiazepines such as diazepam and clonazepam.30
Parting Notes
Not all drugs have a half-life. Some, such as alcohol, follow zero order kinetics. That is, they are metabolized at a fixed rate regardless of how much of the drug is present in the body. In the case of alcohol, this can range from a low of 4–5 g/h in persons with liver disease or malnutrition to 6–8 g/h in healthy persons who consume moderate quantities of alcohol under nonfasting conditions to 12–17 g/h in alcoholics undergoing detoxification or after heavy bouts of drinking.31
Predicting drug elimination based on half-life can go awry when very high doses of drugs are used,32 as in the case of fluoxetine and the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder and when drugs are consumed in overdose; in the latter circumstance, saturation of metabolism may be the explanation.33
Published online: July 25, 2022.
 Each month in his online column, Dr Andrade considers theoretical and practical ideas in clinical psychopharmacology with a view to update the knowledge and skills of medical practitioners who treat patients with psychiatric conditions.
Each month in his online column, Dr Andrade considers theoretical and practical ideas in clinical psychopharmacology with a view to update the knowledge and skills of medical practitioners who treat patients with psychiatric conditions.
Department of Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neurotoxicology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India ([email protected]).
References (33)

- Greenblatt DJ. Basic pharmacokinetic principles and their application to psychotropic drugs. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993;54(suppl):8–13, discussion 55–56. PubMed
- Buxton ILO. Pharmacokinetics: the dynamics of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. In: Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 13th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2018:13–30.
- Rambeck B, Wolf P. Lamotrigine clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1993;25(6):433–443. PubMed CrossRef
- Sproule BA, Hazra M, Pollock BG. Desvenlafaxine succinate for major depressive disorder. Drugs Today (Barc). 2008;44(7):475–487. PubMed CrossRef
- Migdalof BH, Grindel JM, Heykants JJ, et al. Penfluridol: a neuroleptic drug designed for long duration of action. Drug Metab Rev. 1979;9(2):281–299. PubMed
- Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Zhang Q, et al. Slow accumulation and elimination of diazepam and its active metabolite with extended treatment in the elderly. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;61(2):193–203. PubMed CrossRef
- Gaedigk A, Sangkuhl K, Whirl-Carrillo M, et al. Prediction of CYP2D6 phenotype from genotype across world populations. Genet Med. 2017;19(1):69–76. PubMed CrossRef
- Heykants J, Huang ML, Mannens G, et al. The pharmacokinetics of risperidone in humans: a summary. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994;55(suppl):13–17. PubMed
- Andrade C. Augmentation of venlafaxine with bupropion: risks associated with a triple monoamine reuptake inhibition approach to partially responsive depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74(2):e119–e121. PubMed CrossRef
- Andrade C. Drugs that escape hepatic metabolism. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73(7):e889–e890. PubMed CrossRef
- Andrade C. Ketamine for depression, 2: diagnostic and contextual indications. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78(5):e555–e558. PubMed CrossRef
- Bertilsson L. Clinical pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978;3(2):128–143. PubMed CrossRef
- Preskorn SH. Clinically relevant pharmacology of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. An overview with emphasis on pharmacokinetics and effects on oxidative drug metabolism. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997;32(suppl 1):1–21. PubMed CrossRef
- Janicak PG. The relevance of clinical pharmacokinetics and therapeutic drug monitoring: anticonvulsant mood stabilizers and antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993;54(suppl):35–41, discussion 55–56. PubMed
- Owen RT. Extended-release paliperidone: efficacy, safety and tolerability profile of a new atypical antipsychotic. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007;43(4):249–258. PubMed CrossRef
- Gomolin IH, Smith C, Jeitner TM. Once-daily memantine: pharmacokinetic and clinical considerations. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(9):1812–1813. PubMed CrossRef
- Schulz JB, Rainer M, Klünemann H-H, et al. Sustained effects of once-daily memantine treatment on cognition and functional communication skills in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: results of a 16-week open-label trial. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;25(3):463–475. PubMed CrossRef
- Gitlin M. Lithium side effects and toxicity: prevalence and management strategies. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2016;4(1):27. PubMed CrossRef
- Callaghan JT, Bergstrom RF, Ptak LR, et al. Olanzapine. pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;37(3):177–193. PubMed CrossRef
- San L, Casillas M, Ciudad A, et al. Olanzapine orally disintegrating tablet: a review of efficacy and compliance. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008;14(3):203–214. PubMed CrossRef
- Green B. Focus on olanzapine. Curr Med Res Opin. 1999;15(2):79–85. PubMed CrossRef
- Balant-Gorgia AE, Gex-Fabry M, Balant LP. Clinical pharmacokinetics of clomipramine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991;20(6):447–462. PubMed CrossRef
- Allsopp LF, Huitson A, Deering RB, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of sustained-release clomipramine (Anafranil SR) in the treatment of phobias: a comparison with the conventional formulation of clomipramine (Anafranil). J Int Med Res. 1985;13(4):203–208. PubMed CrossRef
- Herrera D, Mayet L, Galindo MC, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a sustained-release dosage form of clomipramine. J Clin Pharmacol. 2000;40(12 Pt 2):1488–1493. PubMed
- Andrade C. Sustained-release, extended-release, and other time-release formulations in neuropsychiatry. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(8):e995–e999. PubMed CrossRef
- Stahl SM, Felker A. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a modern guide to an unrequited class of antidepressants. CNS Spectr. 2008;13(10):855–871. PubMed CrossRef
- Grady MM, Stahl SM. Practical guide for prescribing MAOIs: debunking myths and removing barriers. CNS Spectr. 2012;17(1):2–10. PubMed CrossRef
- Weiden PJ, Kim E, Bermak J, et al. Does half-life matter after antipsychotic discontinuation? a relapse comparison in schizophrenia with 3 different formulations of paliperidone. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78(7):e813–e820. PubMed CrossRef
- Gopal S, Gassmann-Mayer C, Palumbo J, et al. Practical guidance for dosing and switching paliperidone palmitate treatment in patients with schizophrenia. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(2):377–387. PubMed CrossRef
- Pétursson H. The benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome. Addiction. 1994;89(11):1455–1459. PubMed CrossRef
- Jones AW. Alcohol, its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in the body and pharmacokinetic calculations. WIREs Forensic Sci. 2019;1(5):e1340. CrossRef
- Prozac. Prescribing information. Eli Lilly; 2006. https://www.google.com/url?esrc=s&q=&rct=j&sa=U&url=https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2006/018936s076lbl.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwj4obOy7ub4AhXLRmwGHVUjDCYQFnoECAoQAg&usg=AOvVaw3eKUJDJ4a8_XERkYPGhvvi. Accessed July 7, 2022.
- Sue YJ, Shannon M. Pharmacokinetics of drugs in overdose. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;23(2):93–105. PubMed CrossRef
This PDF is free for all visitors!
Save
Cite