Objective: This study evaluated the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of aripiprazole lauroxil, a novel long-acting injectable atypical antipsychotic, for the treatment of schizophrenia.
Method: An international multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted between December 2011 and March 2014. Patients (N = 623) aged 18 to 70 years with schizophrenia (DSM-IV-TR criteria), experiencing an acute exacerbation, were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive gluteal intramuscular injection of aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg, aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg, or matching placebo once monthly for 12 weeks. The primary efficacy outcome was change in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score from baseline to day 85. The Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-I) score at day 85 was the secondary efficacy outcome. Safety and tolerability were assessed.
Results: The PANSS total score (mean ± standard error [SE]) improved significantly from baseline to day 85 in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 882 mg groups, with placebo-adjusted differences of −10.9 ± 1.8 (P < .001) and −11.9 ± 1.8 (P < .001), respectively. Significant (P ≤ .004) improvements in both active treatment groups were demonstrated as early as day 8 and continued throughout the treatment period. The proportion of patients who were very much or much improved on the CGI-I was significantly greater with aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 882 mg treatment versus placebo (P < .001). The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were insomnia, akathisia, headache, and anxiety. The incidence of injection site reactions was low, predominantly described as injection site pain, and was associated with the first injection.
Conclusions: Aripiprazole lauroxil demonstrated robust efficacy for treatment of patients experiencing acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. The improvement in psychotic symptoms was statistically significant and clinically meaningful. Symptom improvement occurred rapidly after initiation of aripiprazole lauroxil treatment and was maintained throughout the study. Both aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 882 mg doses were well tolerated. These results support aripiprazole lauroxil as an important new treatment option for schizophrenia.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01469039; Clinicaltrialsregister.eu identifier: 2012-003445-15
This work may not be copied, distributed, displayed, published, reproduced, transmitted, modified, posted, sold, licensed, or used for commercial purposes. By downloading this file, you are agreeing to the publisher’s Terms & Conditions.
ABSTRACT
Objective: This study evaluated the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of aripiprazole lauroxil, a novel long-acting injectable atypical antipsychotic, for the treatment of schizophrenia.
Method: An international multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted between December 2011 and March 2014. Patients (N = 623) aged 18 to 70 years with schizophrenia (DSM-IV-TR criteria), experiencing an acute exacerbation, were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive gluteal intramuscular injection of aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg, aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg, or matching placebo once monthly for 12 weeks. The primary efficacy outcome was change in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score from baseline to day 85. The Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-I) score at day 85 was the secondary efficacy outcome. Safety and tolerability were assessed.
Results: The PANSS total score (mean ± standard error [SE]) improved significantly from baseline to day 85 in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 882 mg groups, with placebo-adjusted differences of −10.9 ± 1.8 (P < .001) and −11.9 ± 1.8 (P < .001), respectively. Significant (P ≤ .004) improvements in both active treatment groups were demonstrated as early as day 8 and continued throughout the treatment period. The proportion of patients who were very much or much improved on the CGI-I was significantly greater with aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 882 mg treatment versus placebo (P < .001). The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were insomnia, akathisia, headache, and anxiety. The incidence of injection site reactions was low, predominantly described as injection site pain, and was associated with the first injection.
Conclusions: Aripiprazole lauroxil demonstrated robust efficacy for treatment of patients experiencing acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. The improvement in psychotic symptoms was statistically significant and clinically meaningful. Symptom improvement occurred rapidly after initiation of aripiprazole lauroxil treatment and was maintained throughout the study. Both aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 882 mg doses were well tolerated. These results support aripiprazole lauroxil as an important new treatment option for schizophrenia.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01469039; Clinicaltrialsregister.eu identifier: 2012-003445-15
J Clin Psychiatry 2015;76(8):1085-1090
© Copyright 2015 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: December 17, 2014; accepted March 19, 2015.
Online ahead of print: June 9, 2015 (doi:10.4088/JCP.14m09741).
Corresponding author: Srdjan Stankovic, MD, MSPH, Alkermes, Inc, 852 Winter St, Waltham, MA 02451 ([email protected]).
Despite the availability of effective medications for the treatment of schizophrenia, approximately 80% of patients relapse within 5 years. Poor adherence has been associated with relapse and worsening of long-term functional and mental outcomes1 and is the most common cause of relapse.2-5 Long-acting injectable (LAI) atypical antipsychotics are an important treatment option for schizophrenia, with demonstrated efficacy in reducing the severity of both positive and negative symptoms. Long-acting antipsychotic formulations were developed to promote greater treatment adherence and improved pharmacokinetics.6 Results from clinical trials have shown comparable or greater efficacy with LAIs than their oral equivalents, and medication adherence consistently improves when patients have switched from an oral to a LAI regimen.7,8 In addition, the sustained dosing and the ability of physicians and caregivers to monitor the regularity and frequency of LAI administration have demonstrated a beneficial impact on patient outcomes.8 Although LAI formulations of some atypical antipsychotics are available, new formulations offer the potential to provide flexibility for patients and providers in terms of dose and dosing interval, differentiated pharmacokinetic profile and tolerability, and ease of administration.
Aripiprazole lauroxil is a novel LAI atypical antipsychotic currently in development for the treatment of schizophrenia. The proprietary technology (LinkeRx) utilized to develop aripiprazole lauroxil allows for controlled release after injection and extends exposure to the active molecule.9 The technology, combined with aripiprazole lauroxil’s unique formulation, allows for multiple dose strengths and dosing intervals, which provides flexibility to address patient heterogeneity and to allow for individualized patient care. Aripiprazole lauroxil doses studied in the clinical development program were designed to be consistent with the range of oral aripiprazole doses (10 to 30 mg) most often used to treat schizophrenia.
Following injection, the biotransformation of aripiprazole lauroxil involves enzyme-mediated hydrolysis to form N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole, which subsequently undergoes water-mediated hydrolysis to aripiprazole. Early clinical development of aripiprazole lauroxil demonstrated aripiprazole plasma concentrations reached maximal levels in 37 to 48 days and persisted for at least 88 days following a single injection. In a study of adults with schizophrenia, repeat dosing of intramuscular gluteal injections of aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg (300-mg aripiprazole equivalent), 662 mg (450-mg aripiprazole equivalent), and 882 mg (600-mg aripiprazole equivalent) resulted in aripiprazole concentrations within the established therapeutic range and were well tolerated (data on file, Alkermes, Inc; Waltham, Massachusetts). In a subsequent study10 in patients with schizophrenia, it was demonstrated that intramuscular injections of aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg given in the deltoid and gluteal muscles resulted in comparable exposure to aripiprazole and were well tolerated. Therefore, this allows for both deltoid and gluteal intramuscular injection sites to be used interchangeably for administration of the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg dose.
The objective of this international, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of once-monthly aripiprazole lauroxil for the treatment of acute exacerbation in patients with schizophrenia.
METHOD
The study was conducted in 7 countries, including the United States, Ukraine, Russia, Bulgaria, Romania, Philippines, and Malaysia, between December 2011 and March 2014 in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, 1964, and Good Clinical Practice principles outlined in the International Conference on Harmonization, 1997. The protocol, amendments, and informed consent were approved by an institutional review board or local ethics committee for each site, and written informed consent of all patients was obtained prior to study participation after the nature of the procedures had been fully explained. This study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (identifier: NCT01469039) and clinicaltrialsregister.eu (identifier: 2012-003445-15).
Study Design
This was an international, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of aripiprazole lauroxil conducted in adult patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Patients initially were evaluated at a screening visit up to 10 days prior to randomization. Patients meeting initial screening eligibility criteria were admitted to an inpatient study unit. Currently prescribed antipsychotics were discontinued after screening and prior to administration of study drug. Aripiprazole-naive patients were given a test dose of oral aripiprazole 5 mg administered daily for 2 days prior to randomization to assess tolerability. Patients who had previously taken and tolerated aripiprazole were not required to undergo the tolerability assessment.

- Long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotics represent an important option for treating schizophrenia, with a significant body of evidence suggesting that LAIs improve adherence markedly, thereby resulting in better outcomes.
- Aripiprazole lauroxil demonstrated robust efficacy with clinically meaningful improvements in schizophrenia symptoms that were demonstrated early in treatment and persisted throughout the study.
- Aripiprazole lauroxil was well tolerated, with a safety profile similar to oral aripiprazole.
Patient Selection
Eligible patients were 18 to 70 years of age and diagnosed with schizophrenia as defined by DSM-IV-TR and confirmed by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Disorders, Clinical Trials version.11 All patients were currently experiencing an acute exacerbation or relapse with onset of < 2 months prior to screening and < 2 weeks’ duration of hospitalization if inpatient at time of screening. Patients also were required to have experienced a clinically beneficial response to treatment with an antipsychotic medication, have never received clozapine, and have been an outpatient for > 3 months during the year prior to enrollment. At screening and baseline, patients were required to have a Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS)12 total score of 70 to 120 and a score of ≥ 4 for ≥ 2 of the selected positive scale items (item 1: delusions; item 2: conceptual disorganization; item 3: hallucinatory behavior; item 6: suspiciousness/persecution). Patients were also required to have a Clinical Global Impressions-Severity of Illness scale (CGI-S)13 score of ≥ 4 (range, 1 = normal [not at all ill] to 7 = among the most extremely ill patients).
Key exclusion criteria included comorbid schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, dementia, delirium, amnestic or any other cognitive disorder currently or within the past 2 years, any clinically significant medical illness or laboratory abnormality, prior inadequate response to oral aripiprazole (unless poor adherence was a contributing factor), LAI antipsychotic treatment within 60 days of screening, diagnosis of substance dependence within 6 months or substance abuse within 3 months of screening, or women who were pregnant, lactating, or breastfeeding.
Study Treatments
Eligible patients were randomized 1:1:1 in a double-blind fashion to aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg (300-mg aripiprazole equivalent), aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg (600-mg aripiprazole equivalent), or placebo (fat emulsion for human use; Intralipid) injected into the gluteal muscle once every 4 weeks (days 1, 29, and 57). The gluteal muscle was selected as the injection site to maintain blinding to study drug since only the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg dose can be administered in the deltoid muscle. Because of the different volumes of the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg and 882-mg doses, patients randomized to placebo were further randomized 1:1 in a double-blind fashion to low- or high-volume placebo. Thus, the overall randomization ratio to aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg, aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg, placebo low volume, and placebo high volume was 2:2:1:1. In addition to intramuscular study drug, patients received oral study drug daily administered in a double-blind fashion for the first 3 weeks after randomization to achieve early therapeutic exposure to aripiprazole from the combined release of aripiprazole lauroxil and oral aripiprazole in the context of a placebo-controlled acute schizophrenia study. Patients randomized to an aripiprazole lauroxil treatment group received oral aripiprazole (15 mg), and patients randomized to placebo received matching oral placebo for 3 weeks after randomization. Patients remained in the inpatient study unit for at least 2 weeks after administration of the first dose of intramuscular study drug and were discharged after the study investigator determined that they were clinically stable. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability were assessed throughout the treatment period. After discharge from the inpatient study unit, outpatient visits occurred at days 22, 29, 43, 57, 71, and 85. Follow-up visits for safety assessments were scheduled to occur at days 113 and 141.
Study Assessments
The PANSS and CGI-S scales were administered at screening and on days 1, 8, 15, 22, 29, 57, and 85. The Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-I)13 was administered at days 8, 15, 22, 29, 57, and 85.
Safety was evaluated based on the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), the incidence of adverse events (AEs) leading to discontinuation, vital sign measurements, physical examination findings, laboratory test results, electrocardiogram findings, and concomitant medications.
Injection site reaction evaluation (pain, erythema, hematoma, discoloration, and induration) was performed following every injection and on days 8 and 15 and every 2 weeks following the second injection and monthly during the follow-up period.
Statistical Methods
Efficacy analyses were performed using data from the full analysis set (FAS; n = 596), defined as all randomized patients who received at least 1 dose of intramuscular study drug and had at least 1 primary efficacy assessment after administration of intramuscular study drug. The primary efficacy end point was the change from baseline to day 85 in PANSS total score and was analyzed using an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) with a last observation carried forward (LOCF) approach in the FAS population. The ANCOVA model included study region and treatment group as factors and baseline PANSS total score as a covariate. The primary efficacy end point was also analyzed using a mixed model for repeated measures (MMRM) in the FAS population as a sensitivity analysis to assess the robustness of the primary efficacy results. The MMRM model included study region, treatment group, visit, and treatment group-by-visit interaction as factors and baseline PANSS total score as a covariate, and an unstructured covariance matrix was used to model within-subject variability. The secondary efficacy end point was the CGI-I score at day 85, which was analyzed using a nonparametric Wilcoxon rank sum test using the LOCF approach. The proportion of patients achieving a CGI-I score of 1 (very much improved) or 2 (much improved) at each assessment was compared with a logistic regression model adjusting for study region as sensitivity analysis. For primary and secondary analyses, each of the aripiprazole lauroxil groups was compared with the placebo group. The Hommel method was used to adjust for multiple comparisons.14 Post hoc analyses were conducted using MMRM to evaluate the effect of aripiprazole lauroxil in patients with greater severity of illness at baseline using the median PANSS score at baseline as the cutoff.
Safety and tolerability analyses were performed using data from the safety population, defined as all patients who received at least 1 dose of intramuscular study drug.
Assuming a common standard deviation of 20, and a dropout rate of approximately 40% and 60% for the treatment and placebo groups, respectively, an estimated sample size of approximately 180 efficacy evaluable patients per treatment group was estimated to provide at least 90% power to detect a 8-point difference in the primary efficacy end point at 2-sided significance level overall of .05, adjusted for 2 comparisons with placebo using the Hommel procedure.14
RESULTS
Patients
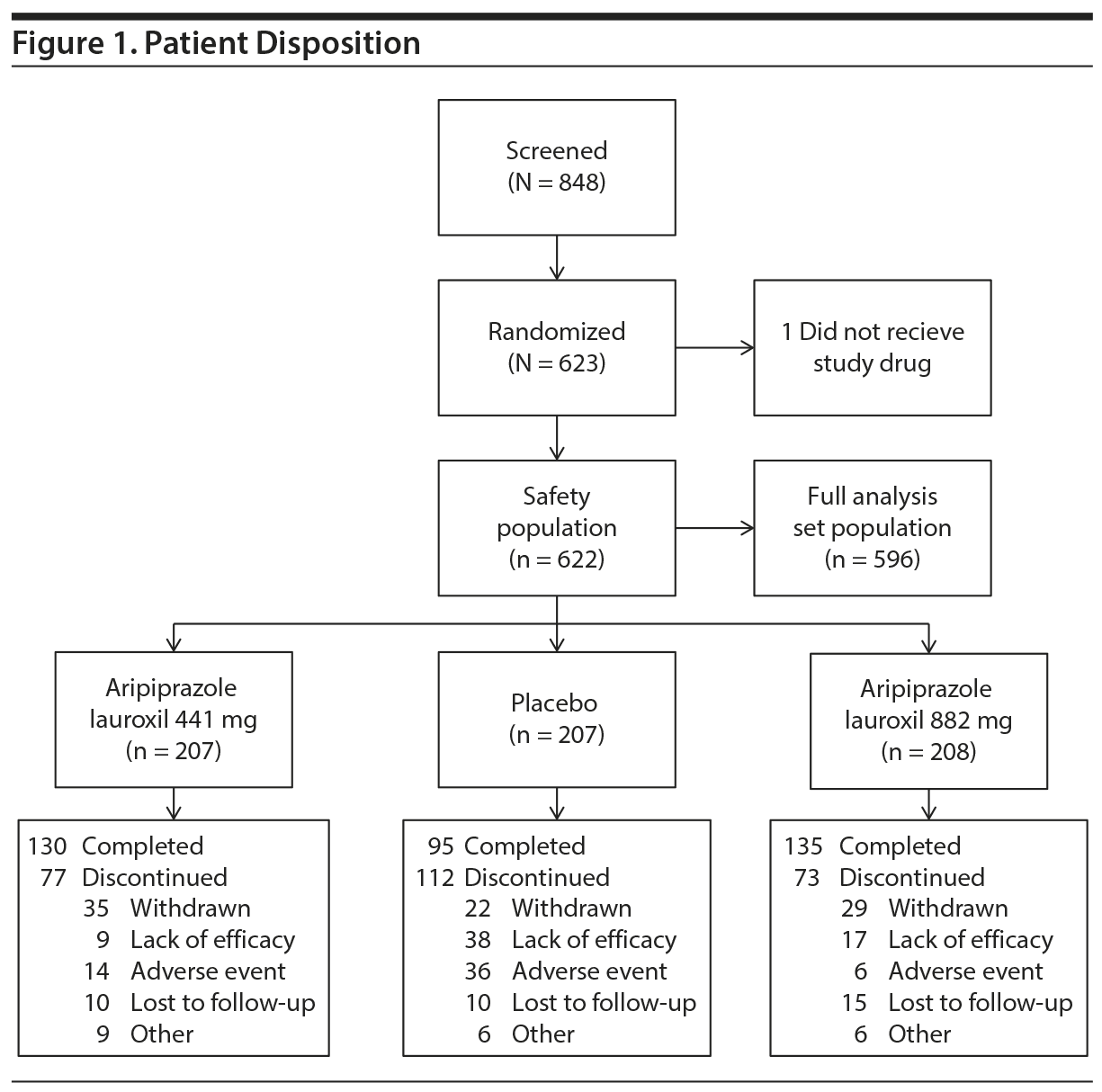
Patient disposition is reported in Figure 1. A total of 848 patients were screened, and 623 were randomized. One patient was randomized but did not receive the study drug due to inclusion/exclusion violation; therefore, 622 patients were included in the safety population. Of these, 596 were included in the FAS population. Overall, the majority of subjects were male (67.9%) with a median age of 39.0 years (Table 1). Subjects were predominantly white (46.7%) or black/African American (39.8%). Most subjects were enrolled in North America (49.3%) or Europe (38.4%). The age, gender, primary race, ethnicity, and region/countries were evenly distributed among the 3 groups. Patients were markedly to severely ill, with PANSS total scores (mean [SD]) of 92.6 (10.2), 92.0 (10.8), and 93.9 (11.3) for the aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg, aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients receiving all 3 intramuscular injections was 65.2% and 67.8% for the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg and 882-mg dose groups, which was statistically significant and higher than 48.3% for placebo (χ2 = 12.06 [P = .0005] and χ2 = 16.17 [P < .0001] for 441 mg and 882 mg, respectively).
Efficacy
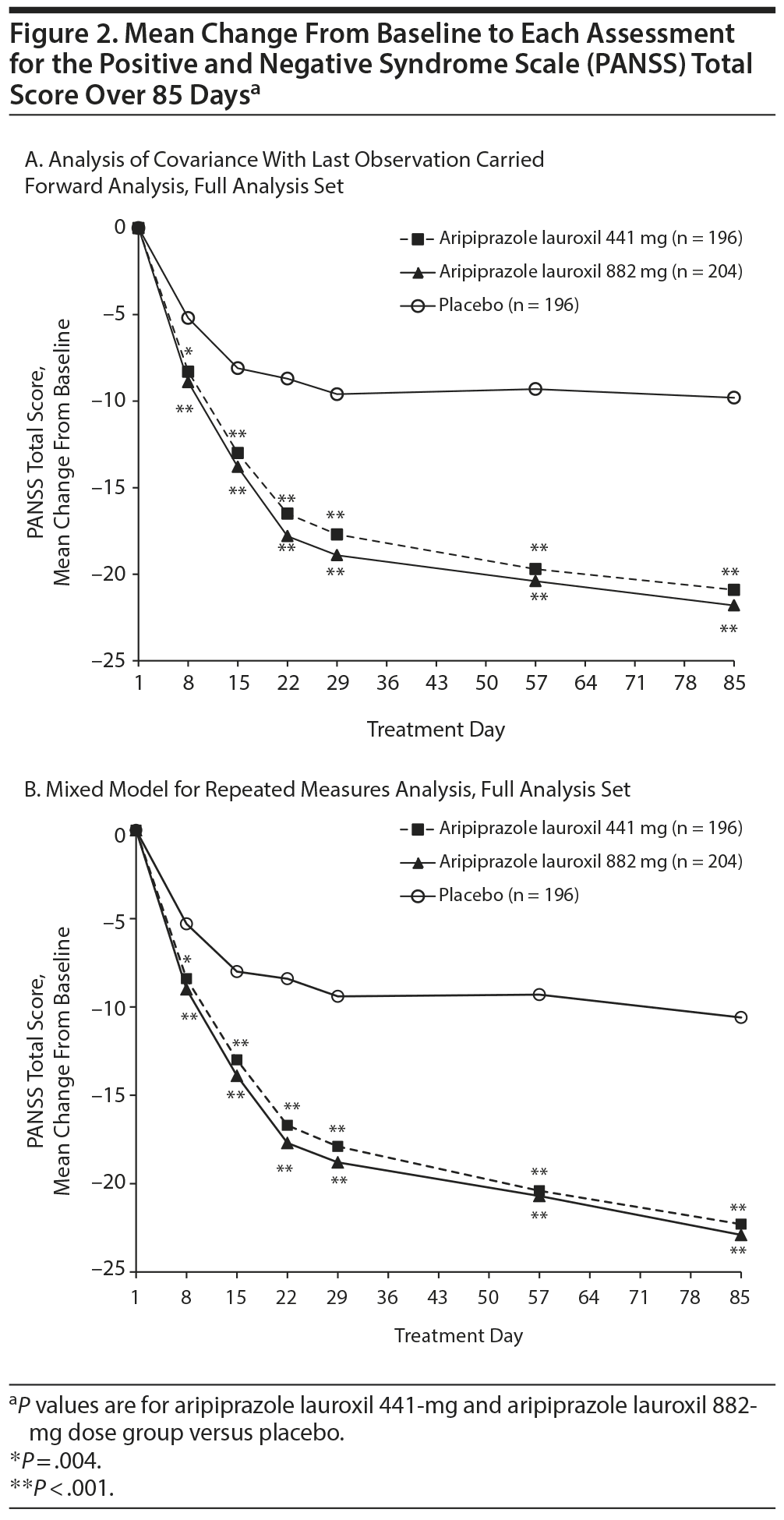
A clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement from baseline to day 85 in PANSS total score was demonstrated for the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg and 882-mg groups, with placebo-adjusted least squares mean differences of −10.9 (1.8) (P < .001) and −11.9 (1.8) (P < .001), respectively (see Supplementary eTable 1 at PSYCHIATRIST.COM). Significant improvements in PANSS total score for both active treatment groups were observed as early as day 8 and continued through the end of the double-blind treatment period in both ANCOVA with LOCF and MMRM approaches (Figure 2). In a post hoc MMRM analysis in a subpopulation of patients with more severe symptoms (baseline median PANSS score of > 92 as cutoff), the observed placebo-adjusted mean change in PANSS total score at day 85 was −14.7 (3.5) for the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg dose group (P < .0001) and −16.6 (3.4) for the 882-mg dose group (P < .0001) (Supplementary eTable 1).
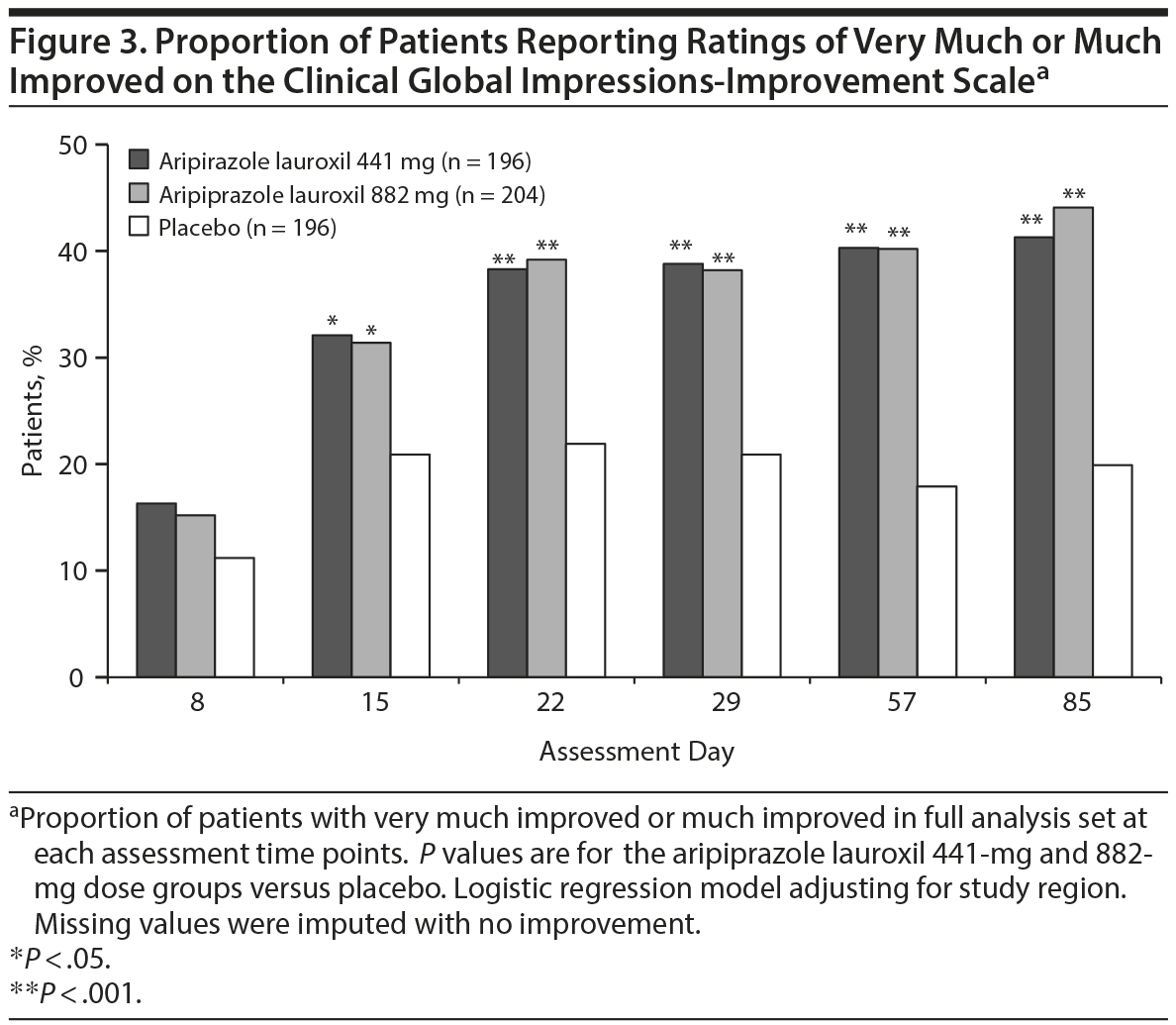
Both aripiprazole lauroxil treatment groups had significantly better CGI-I scores at day 85 compared to placebo (P < .001) using Wilcoxon rank sum test. The proportion of patients who were very much or much improved was also significantly greater in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg and 882-mg groups compared to placebo at all assessments after day 8 (P < .05 to P < .001; Figure 3).
Safety and Tolerability
Overall, the incidence of most AEs was similar among groups, and AEs were mild or moderate in intensity. Serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported in 11 patients during the treatment period: 3 (1.4%), 4 (1.9%), and 4 (1.9%) in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg, 882-mg, and placebo groups, respectively, including 1 death (victim of homicide) in the placebo group. Only 1 SAE, which was reported in a patient with akathisia in the aripiprazole lauroxil 882-mg dose group, was considered related to the study drug. No individual SAE was reported by more than 1 patient. Severe TEAEs were similar across the 3 groups and were reported in 9 (4.3%), 9 (4.3%), and 12 (5.8%) of patients in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg, 882-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. More patients in the placebo group discontinued due to AEs (17.9%) than patients in either aripiprazole lauroxil group (6.8% for 441 mg and 2.9% for 882 mg), which was attributed to exacerbation of the underlying illness.
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurring in ≥ 2% of patients in the aripiprazole lauroxil treatment groups are reported in Table 2. The most common TEAEs occurring in > 5% of patients in the aripiprazole lauroxil groups were insomnia, akathisia, headache, and anxiety. Akathisia was the only TEAE with an incidence of ≥ 5% in each aripiprazole lauroxil group that was at least twice the rate of placebo (11.6%, 11.5%, and 4.3%). The majority (> 75%) of all akathisia episodes occurred before the second injection, generally within the first 3 weeks, when the patients in the aripiprazole lauroxil groups were also receiving oral aripiprazole. There were 3 cases of akathisia that occurred after the second injection in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg group and 1 case in the placebo group. No cases of akathisia occurred in the aripiprazole lauroxil 882-mg group beyond 1 month after the first injection.
The incidence of injection site reactions was low overall, occurring in 8 (3.9%), 12 (5.8%), and 4 (1.9%) patients in the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg, 882-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Pain was the most common description used for injection site reactions, 7 (3.4%), 10 (4.8%), and 4 (1.9%) for the aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg, 882-mg, and placebo groups, respectively, with very few reports of swelling, redness or induration, or other reaction. Most reports of injection site pain were associated with the first injection (Supplementary eFigure 1).
DISCUSSION
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial demonstrated the robust efficacy of aripiprazole lauroxil, a novel, LAI atypical antipsychotic for treatment of schizophrenia. Significant improvement in schizophrenia symptoms was evident as early as day 8 and was maintained throughout the 12-week treatment period. Both aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg and 882-mg doses were well tolerated.
The placebo-adjusted improvement in PANSS total score from baseline to the end of the study was clinically meaningful and statistically significant for both aripiprazole lauroxil dose groups tested, and indeed, the somewhat larger effects demonstrated in the more severely ill patient population (> 92 PANSS total score at baseline) further demonstrate the robust efficacy of both doses of aripiprazole lauroxil. The severity of illness as measured by the PANSS total score was also significantly improved at the end of the treatment period for the aripiprazole lauroxil groups compared to placebo. In addition, early and durable improvement in the CGI-I categories of very much improved or much improved occurred more frequently in the aripiprazole lauroxil patients compared to placebo. Consistent positive findings in sensitivity analysis for the PANSS primary outcome and the CGI-I secondary outcome measures further support the robust efficacy of aripiprazole lauroxil treatment. In addition, given that fewer patients in the placebo group received all 3 injections compared to the aripiprazole lauroxil groups, the treatment effect of aripiprazole lauroxil may have been underestimated as a result of the greater number of dropouts in the placebo group due to lack of efficacy.
The results of the present study are similar to reports of other randomized controlled trials examining the efficacy of LAI atypical antipsychotics in patients with chronic stable schizophrenia and those experiencing acute exacerbations.15-17 The greater improvement observed in the PANSS total score associated with aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg compared to aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg in the subpopulation of more severe patients (mean [SD] PANSS score > 92 at baseline, 101.3 [6.0] for aripiprazole lauroxil 441 mg and 101.0 [6.4] for aripiprazole lauroxil 882 mg) suggests there may potentially be an additional benefit of the higher dose in patients experiencing more severe symptoms.
Both aripiprazole lauroxil 441-mg and 882-mg doses were well tolerated, with a side effect profile consistent with oral aripiprazole. The overall incidence of TEAEs was low and did not appear to be dose dependent. Akathisia was the only common TEAE occurring in at least 5% of treated patients with an incidence greater than twice that of placebo. However, akathisia tended to occur during the initial phase of the study when patients were treated with both oral aripiprazole and aripiprazole lauroxil. This combined exposure may have been a contributing factor, as akathisia is a known side effect of aripiprazole. The incidence of injection site reactions was low, mainly injection site pain, which resolved after the first treatment.
Aripiprazole lauroxil is a novel LAI atypical antipsychotic with multiple safe and effective doses and the ability to be administered in either the deltoid (441-mg dose only) or gluteal muscles as demonstrated in a phase 1 study.10 These characteristics may allow for individualized treatment to meet patient needs.
This study evaluated efficacy and safety of 2 fixed-dose regimens of aripiprazole lauroxil with no opportunity for dose adjustments over the course of the study. It is possible, therefore, that some patients might have benefited more from dose adjustment and flexible dosing. This should be further evaluated in future studies.
In summary, this study demonstrated robust efficacy of multiple doses of aripiprazole lauroxil with a safety and tolerability profile similar to oral aripiprazole. The clinical profile of aripiprazole lauroxil combined with the flexibility afforded by the novel technology and ability to administer in the deltoid and gluteal muscles may represent a new treatment option for both clinicians and their patients with schizophrenia.
Drug names: aripiprazole (Abilify and others), clozapine (Clozaril, FazaClo, and others).
Author affiliations: Department of Psychiatry and Physiology, Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois (Dr Meltzer); Alkermes, Inc, Waltham, Massachusetts (Drs Risinger, Du, Bose, Stankovic, Silverman, and Ehrich and Mss Zummo and Corey); and Department of Neurology and Psychiatry, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri (Dr Nasrallah).
Potential conflicts of interest: Dr Meltzer is a consultant to Alkermes, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Auspex, Naurex, Novartis, and ProPhase; receives grant/research support from Dainippon Sumitomo, FORUM, Naurex, Astellas, Otsuka, Reviva, SureGene, and Sunovion; has received honoraria from Dainippon Sumitomo, FORUM, Naurex, Astellas, Otsuka, Reviva, SureGene, and Sunovion; has served on speakers or advisory boards for Sunovion, Novartis, Reviva, ProPhase, Auspex, and FORUM; and is a stockholder in SureGene and AstraZeneca. Dr Nasrallah is a consultant to, has received honoraria from, and serves on speaker or advisory boards for Alkermes, Genentech, FORUM, Janssen, Merck, Otsuka, Sunovion, and Teva; and has received grant/research support from Forest, Genentech, and FORUM. Drs Risinger, Du, Bose, Stankovic, Silverman, and Ehrich and Mss Zummo and Corey are employees of and hold stock in Alkermes.
Funding/support: The study was sponsored by Alkermes, Inc. Financial support for editorial assistance was provided by Alkermes.
Role of the sponsor: The sponsor was involved in the design, collection, and analysis of the data. Interpretation of the results was by the authors, and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry was made by the authors.
Previous presentation: The study data were first presented as a poster (#75) at the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology Annual Meeting; June 16-19, 2014; Hollywood, Florida.
Acknowledgments: Jennifer E. Layne, PhD, of Alkermes, Inc, provided writing support and interpretation, and Richard S. Perry, PharmD (RP Consulting), provided editorial assistance in the preparation of this article under the direction of the authors. INC Research LLC provided support in conducting the study, and Patrick Cadigan, MD (INC Research), provided medical and safety monitoring, which were supported by the sponsor.
Supplementary material: Available at PSYCHIATRIST.COM.
REFERENCES
1. Ascher-Svanum H, Faries DE, Zhu B, et al. Medication adherence and long-term functional outcomes in the treatment of schizophrenia in usual care. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(3):453-460. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.v67n0317
2. Leucht S, Tardy M, Komossa K, et al. Antipsychotic drugs versus placebo for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;379(9831):2063-2071. PubMed doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60239-6
3. Lindenmayer JP, Liu-Seifert H, Kulkarni PM, et al. Medication nonadherence and treatment outcome in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder with suboptimal prior response. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(7):990-996. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.08m04221
4. Patel MX, Taylor M, David AS. Antipsychotic long-acting injections: mind the gap. Br J Psychiatry suppl. 2009;52(52):S1-S4. PubMed doi:10.1192/bjp.195.52.s1
5. Tiihonen J, Haukka J, Taylor M, et al. A nationwide cohort study of oral and depot antipsychotics after first hospitalization for schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(6):603-609. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10081224
6. Kane JM. Treatment strategies to prevent relapse and encourage remission. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(suppl 14):27-30. PubMed
7. Kishimoto T, Nitta M, Borenstein M, et al. Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of mirror-image studies. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74(10):957-965. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.13r08440
8. Zhornitsky S, Stip E. Oral versus long-acting injectable antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia and special populations at risk for treatment nonadherence: a systematic review. Schizophr Res Treatment. 2012;2012:407171. PubMed doi:10.1155/2012/407171
9. Remenar JF. Making the leap from daily oral dosing to long-acting injectables: lessons from the antipsychotics. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(6): 1739-1749. PubMed doi:10.1021/mp500070m
10. Turncliff R, Hard M, Du Y, et al. Relative bioavailability and safety of aripiprazole lauroxil, a novel once-monthly, long-acting injectable atypical antipsychotic, following deltoid and gluteal administration in adult subjects with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2014;159(2-3):404-410. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.021
11. First MB, Williams JBW, Spitzer RL, et al. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Clinical Trials Version (SCID-CT). New York, NY: Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute; 2007.
12. Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(2):261-276. PubMed doi:10.1093/schbul/13.2.261
13. Guy W. The clinician global severity and impression scales. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Superintendent of Documents, US Government Printing Office, Publication No. 76-338. Washington, DC: US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare. 1976:218-222.
14. Hommel G. A stage wise rejective multiple test procedure based on a modified Bonferroni test. Biometrika. 1988;75(2):383-386. doi:10.1093/biomet/75.2.383
15. Fleischhacker WW, Sanchez R, Perry PP, et al. Aripiprazole once-monthly for treatment of schizophrenia: double-blind, randomised, non-inferiority study. Br J Psychiatry. 2014;205(2):135-144. PubMed doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.113.134213
16. Kane JM, Sanchez R, Perry PP, et al. Aripiprazole intramuscular depot as maintenance treatment in patients with schizophrenia: a 52-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73(5):617-624. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.11m07530
17. Kane JM, Peters-Strickland T, Baker RA, et al. Aripiprazole once-monthly in the acute treatment of schizophrenia: findings from a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75(11):1254-1260. PubMed doi:10.4088/JCP.14m09168
This PDF is free for all visitors!
Save
Cite