Because this piece does not have an abstract, we have provided for your benefit the first 3 sentences of the full text.
Valproate (valproic acid), a well-established anticonvulsant, is principally effective in bipolar disorder. In addition, valproate has been used for the management of a range of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia, personality disorder, anxiety, and agitation in dementia.
The need for therapeutic drug monitoring of valproate in the treatment of epilepsy has been demonstrated.
This work may not be copied, distributed, displayed, published, reproduced, transmitted, modified, posted, sold, licensed, or used for commercial purposes. By downloading this file, you are agreeing to the publisher’s Terms & Conditions.

Valproate Intoxication in a Patient With Blood Valproate Levels Within Therapeutic Range
Valproate (valproic acid), a well-established anticonvulsant, is principally effective in bipolar disorder.1-4 In addition, valproate has been used for the management of a range of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia, personality disorder, anxiety, and agitation in dementia.4-6
The need for therapeutic drug monitoring of valproate in the treatment of epilepsy has been demonstrated. A plasma trough concentration exceeding 50 mg/L is advised in order to reach therapeutic effects on epilepsy, and trough levels exceeding 100-120 mg/L are associated with toxicity and occurrence of adverse events.6-11 There is no clear concentration-response relationship for valproate in most psychiatric conditions. However, the range recommended in the literature for acute mania is 45-125 mg/L in adult patients and 65-90 mg/L in older patients; in maintenance therapy, blood levels of 55-115 mg/L have been recommended.12-15 For this report, we used the ranges advised by our national guidelines16: 60-80 mg/L in maintenance therapy and 80-120 mg/L in acute episodes.
We present a case in which signs of valproate intoxication were clinically present, although the valproate trough concentrations were considered therapeutic (60-120 mg/L).
Case report. Ms A, a 78-year-old woman, was admitted to a geriatric psychiatry ward because of psychosis with manic features. The patient’s psychiatric history revealed schizoaffective disorder (DSM-5 criteria), and her somatic history included a stroke, metabolic syndrome, and chronic renal insufficiency. Psychiatric examination showed high speed in thinking, delusions, command auditory hallucinations, and a euphoric mood. Physical examination showed no abnormalities besides obesity and hyperkinesia due to haloperidol. Laboratory tests showed chronic renal insufficiency (clearance of 59 mL/min/1.73 m2 [reference > 90 mL/min/1.73 m2]).
Prescription of lithium carbonate was not the first choice due to lack of efficacy in the past and side effects (tremor and decline of renal function) in combination with the current reduced renal function. Ms A’s manic psychosis was treated with valproate and haloperidol. Valproate was dosed according to the patient’s body weight in a ratio of 20 mg/kg, which resulted in a daily dosage of 2,100 mg.
Two weeks later, she developed a fluctuating mental status with complaints of sedation, vertigo, and insecurity in walking with falling. Physical examination revealed no new abnormalities, and laboratory tests showed a serum albumin level of 26 g/L (reference, 35-50 g/L) and a plasma trough concentration of 91.9 mg/L (reference, 60-120 mg/L). In medication review by the pharmacist, a free protein unbound trough concentration level of valproate was determined at 34.7 mg/L (reference, 4-12 mg/L). Adjusting the daily valproate dosage to 600 mg resulted in a total valproate level of 49.9 mg/L and a free concentration of 6.1 mg/L (4-12 mg/L). The patient’s vertigo, falling, and sedation resolved within 1 week, while the manic and psychotic features diminished.
This case demonstrates that valproate intoxication can be present despite a therapeutic dosage and a total valproate level within reference range. Symptoms of sedation, vertigo, and insecurity in walking could be attributed to a high protein-unbound plasma concentration of valproate.
Valproate is highly protein bound (mainly albumin) and limited primarily to the extracellular space, with a small (0.1-0.5 L/kg) volume of distribution (Vd). At levels exceeding 90 mg/L and in overdose, saturation of protein-binding sites occurs, resulting in a greater circulating free fraction of valproate and a larger Vd.17 In elderly individuals, valproate elimination half-life is prolonged, which results from a greater Vd, probably due to an increased ratio of fat to lean tissue.18,19 Concomitant therapy can influence valproate levels via induction or inhibition of cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes.19-21
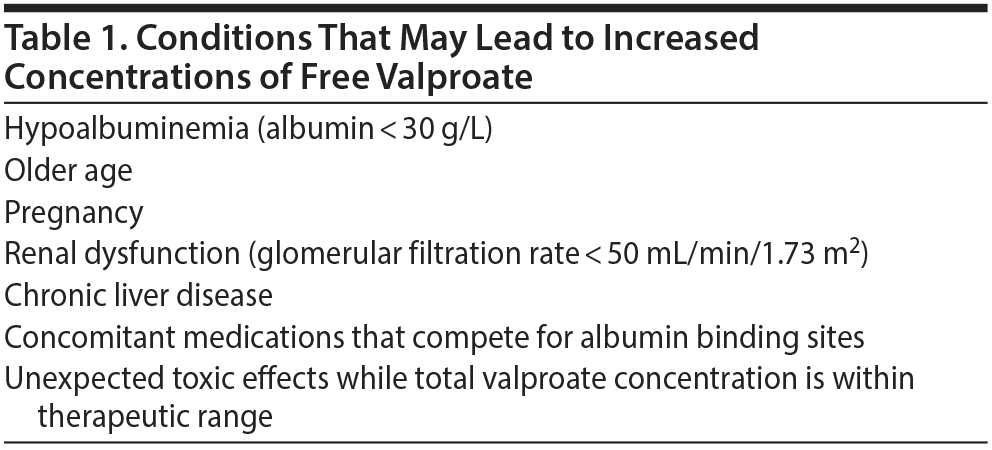
Only unbound drug is pharmacologically active. High free plasma concentrations of valproate may lead to valproate toxicity and adverse effects. In most cases, it is sufficient, and more feasible, to measure total serum concentration of valproate, because there is a known fixed ratio between unbound and total valproate concentration. In most patients, the free fraction of valproate is about 10%. However, an increased free fraction of valproate may be present in some patient groups, resulting in drug toxicity even if the concentration of total drug is within therapeutic range7,8,22,23 (Table 1).
In our opinion, measurement of free valproate concentrations is not needed routinely. However, as shown in our case, there are patients who have both therapeutic total valproate levels and intoxication symptoms due to a high free valproate level. We suggest considering determination of free valproate concentration in those patients who are at risk for developing toxic concentrations of free valproate8,24 (see Table 1).
Submitted: June 4, 2015; accepted October 31, 2016.
Potential conflicts of interest: None.
Funding/support: None.
REFERENCES
1. Bowden CL, Janicak PG, Orsulak P, et al. Relation of serum valproate concentration to response in mania. Am J Psychiatry. 1996;153(6):765-770. PubMed doi:10.1176/ajp.153.6.765
2. Bowden CL, Singh V. Valproate in bipolar disorder: 2000 onwards. Acta Psychiatr Scand suppl. 2005;111(426):13-20. PubMed doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2005.00522.x
3. Allen MH, Hirschfeld RM, Wozniak PJ, et al. Linear relationship of valproate serum concentration to response and optimal serum levels for acute mania. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(2):272-275. PubMed doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.163.2.272
4. Bowden CL. Spectrum of effectiveness of valproate in neuropsychiatry. Expert Rev Neurother. 2007;7(1):9-16. PubMed doi:10.1586/14737175.7.1.9
5. Niedermier JA, Nasrallah HA. Clinical correlates of response to valproate in geriatric inpatients. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1998;10(4):165-168. PubMed doi:10.3109/10401239809147033
6. Fleming J, Chetty M. Therapeutic monitoring of valproate in psychiatry: how far have we progressed? Clin Neuropharmacol. 2006;29(6):350-360. PubMed doi:10.1097/01.WNF.0000228209.69524.E8
7. Barre J, Didey F, Delion F, et al. Problems in therapeutic drug monitoring: free drug level monitoring. Ther Drug Monit. 1988;10(2):133-143. PubMed doi:10.1097/00007691-198802000-00002
8. Dasgupta A. Usefulness of monitoring free (unbound) concentrations of therapeutic drugs in patient management. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;377(1-2):1-13. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.cca.2006.08.026
9. Chateauvieux C, Morceau F, Dicato M, et al. Molecular and therapeutic potential and toxicity of valproic acid. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:1-18. doi:10.1155/2010/479364
10. Walstra GJM. Reversible dementia due to valproic acid therapy [in Dutch]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1997;141(8):391-393. PubMed
11. Armon C, Shin C, Miller P, et al. Reversible Parkinsonism and cognitive impairment with chronic valproate use. Neurology. 1996;47(3):626-635. PubMed doi:10.1212/WNL.47.3.626
12. Pope HG Jr, McElroy SL, Keck PE Jr, et al. Valproate in the treatment of acute mania: a placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991;48(1):62-68. PubMed doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810250064008
13. Bowden CL, Brugger AM, Swann AC, et al; The Depakote Mania Study Group. Efficacy of divalproex vs lithium and placebo in the treatment of mania. JAMA. 1994;271(12):918-924. PubMed doi:10.1001/jama.1994.03510360044034
14. Davis LL, Bartolucci A, Petty F. Divalproex in the treatment of bipolar depression: a placebo-controlled study. J Affect Disord. 2005;85(3):259-266. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.jad.2004.09.009
15. Bowden CL, Calabrese JR, McElroy SL, et al; Divalproex Maintenance Study Group. A randomized, placebo-controlled 12-month trial of divalproex and lithium in treatment of outpatients with bipolar I disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(5):481-489. PubMed doi:10.1001/archpsyc.57.5.481
16. Richtlijn Bipolaire Stoornis. Utrecht, Netherlands: Nederlandse Vereniging voor Psychiatrie; 2015.
17. Olson KR, ed. Poisoning & Drug Overdose. 6th ed. San Francisco, CA: McGraw-Hill Companies; 2012:393-395.
18. Bryson SM, Verma N, Scott PJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics of valproic acid in young and elderly subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;16(1):104-105. PubMed doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02151.x
19. Lampon N, Tutor JC. Apparent clearance of valproic acid in elderly epileptic patients: estimation of the confounding effect of albumin concentration. Ups J Med Sci. 2012;117(1):41-46. PubMed doi:10.3109/03009734.2011.640412
20. Fattore C, Messina S, Battino D, et al. The influence of old age and enzyme inducing comedication on the pharmacokinetics of valproic acid at steady-state: a case-matched evaluation based on therapeutic drug monitoring data. Epilepsy Res. 2006;70(2-3):153-160. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.04.002
21. Perucca E, Grimaldi R, et al. Pharmacokinetics of valproic acid in the elderly. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;17:665-669. PubMed
22. Chan K, Beran RG. Value of therapeutic drug level monitoring and unbound (free) levels. Seizure. 2008;17(6):572-575. PubMed doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2007.12.007
23. Dasgupta A. Clinical utility of free drug monitoring. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002;40(10):986-993. PubMed doi:10.1515/CCLM.2002.172
24. Warner A, Privitera M, Bates D; National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry. Standards of laboratory practice: antiepileptic drug monitoring. Clin Chem. 1998;44(5):1085-1095. PubMed
aDepartment of Old Age Psychiatry, Pro Persona, Arnhem/Nijmegen/Wolfheze, the Netherlands
bDepartment of Clinical Pharmacy, Rijnstate Hospital, Arnhem, the Netherlands
*Corresponding author: Johanna E. M. P. Smits, MD, Pro Persona, Department of Old Age Psychiatry, Panovenlaan 25 DZ Nijmegen, The Netherlands ([email protected]).
J Clin Psychiatry 2017;78(4):e413-e414
https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.15cr10147
© Copyright 2017 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
This PDF is free for all visitors!
Save
Cite