Background: Insomnia is symptomatic of most psychiatric disorders. Non-habit-forming agents such as trazodone and quetiapine are commonly used off-label to treat patients with insomnia. The safety and efficacy of trazodone and quetiapine as medications for treatment of insomnia have never been directly contrasted. The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of trazodone to quetiapine among inpatient psychiatric patients by measuring the traditional sleep parameters of total sleep time, number of nighttime awakenings, sleep efficiency, sleep latency, length of hospitalization, and patient-reported side effects.
Method: Participants were recruited from St Helena Hospital Center for Behavioral Health, Vallejo, California. Patient inclusion criteria were age 18 to 65 years, admitted between September 2011 and February 2012, and a physician order for trazodone or quetiapine for insomnia. Exclusion criteria included primary insomnia, pregnancy, concomitant order of trazodone and quetiapine, receiving trazodone or quetiapine up to 2 weeks prior to the study, and inability to coherently communicate. Subjective patient interviews and objective nursing sleep log reviews composed the data set.
Results: On average, mean total sleep time hours were longer among patients receiving trazodone versus those receiving quetiapine according to patients’ subjective reports (7.80 vs 6.75, respectively, P < .01) and the nursing sleep logs (9.13 vs 8.68, respectively, P = .04). Patients receiving trazodone experienced fewer mean nighttime awakenings versus those receiving quetiapine (0.52 vs 0.75, respectively, P = .04) according to the nursing sleep log report. Patients receiving trazodone reported more side effects of constipation, nausea, and diarrhea than patients receiving quetiapine.
Conclusions: With respect to total sleep time and nighttime awakenings, trazodone was a more effective alternative than quetiapine. However, patients receiving trazodone experienced more gastrointestinal patient-reported side effects.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2013;15(6):doi:10.4088/PCC.13m01558
© Copyright 2013 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: July 18, 2013; accepted August 14, 2013.
Published online: November 7, 2013.
Corresponding author: Shadi Doroudgar, PharmD, 1310 Club Dr, Vallejo, CA 94594 ([email protected]).
Evaluation of Trazodone and Quetiapine for Insomnia:
An Observational Study in Psychiatric Inpatients
ABSTRACT
Background: Insomnia is symptomatic of most psychiatric disorders. Non–habit-forming agents such as trazodone and quetiapine are commonly used off-label to treat patients with insomnia. The safety and efficacy of trazodone and quetiapine as medications for treatment of insomnia have never been directly contrasted. The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of trazodone to quetiapine among inpatient psychiatric patients by measuring the traditional sleep parameters of total sleep time, number of nighttime awakenings, sleep efficiency, sleep latency, length of hospitalization, and patient-reported side effects.
Method: Participants were recruited from St Helena Hospital Center for Behavioral Health, Vallejo, California. Patient inclusion criteria were age 18 to 65 years, admitted between September 2011 and February 2012, and a physician order for trazodone or quetiapine for insomnia. Exclusion criteria included primary insomnia, pregnancy, concomitant order of trazodone and quetiapine, receiving trazodone or quetiapine up to 2 weeks prior to the study, and inability to coherently communicate. Subjective patient interviews and objective nursing sleep log reviews composed the data set.
Results: On average, mean total sleep time hours were longer among patients receiving trazodone versus those receiving quetiapine according to patients’ subjective reports (7.80 vs 6.75, respectively, P < .01) and the nursing sleep logs (9.13 vs 8.68, respectively, P = .04). Patients receiving trazodone experienced fewer mean nighttime awakenings versus those receiving quetiapine (0.52 vs 0.75, respectively, P = .04) according to the nursing sleep log report. Patients receiving trazodone reported more side effects of constipation, nausea, and diarrhea than patients receiving quetiapine.
Conclusions: With respect to total sleep time and nighttime awakenings, trazodone was a more effective alternative than quetiapine. However, patients receiving trazodone experienced more gastrointestinal patient-reported side effects.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2013;15(6):doi:10.4088/PCC.13m01558
© Copyright 2013 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
Submitted: July 18, 2013; accepted August 14, 2013.
Published online: November 7, 2013.
Corresponding author: Shadi Doroudgar, PharmD, 1310 Club Dr, Vallejo, CA 94594 ([email protected]).
Insomnia is a common medical complaint. It is the most prevalent sleep disorder, occurring in 19%1 to 50% of clinic patients seeking treatment for other complaints in the primary care or specialty care setting.2,3 One study noted that the prevalence of insomnia was as high as 69% in primary care patients.4 A national survey of noninstitutionalized adults reported a 35% insomnia prevalence rate during the course of the previous year, with insomnia occurring about 50% more often in women.5 About 20% to 36% of patients are affected by insomnia chronically and report insomnia duration of greater than 1 year.6–10 One of the predictive variables for insomnia is the presence of comorbid psychiatric illness.11,12 Additionally, insomnia is a feature of many psychiatric disorders, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and psychosis,13 which explains the high number of patients who suffer from insomnia in the inpatient psychiatric setting.
Pharmacologically, many agents are used to induce sleep. Benzodiazepines and non–benzodiazepine hypnotics, such as zolpidem and eszopiclone, are commonly prescribed. However, these drugs are habit forming and may lead to abuse if used long-term.14 In addition, use of benzodiazepines is associated with multiple central nervous system–related side effects, including ataxia, falls, and memory impairment (anterograde amnesia), and has led to increases in motor vehicle accidents.15–17
Additionally, due to the habit-forming nature of benzodiazepines and non–benzodiazepine hypnotics, other agents are often used first-line for patients’ insomnia. Over-the-counter antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and doxylamine are commonly used since it is well known that blockade of the histamine-1 (H1) receptor leads to sedation. However, antihistamines may not be appropriate for many patients due to potential risks of central and peripheral anticholinergic side effects. Additionally, anticholinergic medications may lead to drug-induced delirium.18 In the inpatient psychiatric setting, quetiapine, a second-generation antipsychotic, and trazodone, a triazolopyridine antidepressant, are among medications without a US Food and Drug Association–approved indication for insomnia. Trazodone is a weak but specific inhibitor of serotonin (5-HT) reuptake and has antagonistic actions at the H1, 5-HT1A, 5-HT1C, and 5-HT2A receptors, as well as the α1-adrenoceptors and α2-adrenoceptors.19 The H1, 5-HT2A, and α1 antagonistic pharmacologic properties make trazodone effective for insomnia, but the α-blocking properties may predispose patients to orthostatic hypotension and priapism.20 Quetiapine acts as an antagonist at serotonin (5-HT1A and 5-HT2A), dopamine (D1 and D2), histamine (H1), and α1– and α2-adrenergic receptors.21 Somnolence, as a result of 5-HT2A, H1, and α1 blockade, is a side effect of low-dose quetiapine that makes it useful in treating insomnia. However, the metabolic adverse effects of quetiapine make its use problematic.
Polysomnography studies have shown that sleep architecture is different in patients with mental illness. For example, sleep in depressed patients tends to be characterized by decreased sleep efficiency, reduction of non–rapid eye movement (NREM) slow-wave sleep, shortening of REM sleep latency, increased REM length, and increased REM density.22,23 Additionally, in patients with schizophrenia, polysomnographic sleep studies have consistently shown decreases in sleep parameters, including total sleep time, sleep efficiency, and REM sleep, with increases in sleep fragmentation and sleep latency.24–27 There is a deficit in the restorative sleep, occurring in NREM stage 3 sleep, in patients with schizophrenia.28 Addressing these sleep deficits and deviations from normal sleep patterns in psychiatric patients could help in reducing symptoms of insomnia that may impact their mental health.
Many studies evaluate trazodone and quetiapine in various patient populations; however, no currently published study compares and contrasts the efficacy of these 2 agents in an acute inpatient setting. This prospective observational study examines trazodone and quetiapine with respect to traditional sleep parameters of total sleep time, sleep efficiency, sleep latency, number of nighttime awakenings, sleep quality, duration of hospitalization, and patient-reported side effects.
METHOD
Participants were recruited from the St Helena Hospital Center for Behavioral Health, Vallejo, California, for this prospective observational effectiveness study. Inclusion criteria were (1) age 18 to 65 years, (2) admission between September 2012 and February 2013 to the Center for Behavioral Health, and (3) a physician’s order at any point during the hospital stay for trazodone or quetiapine. Exclusion criteria included (1) diagnosis of primary insomnia, (2) pregnancy, (3) simultaneous administration of both study medications, (4) receiving either trazodone or quetiapine up to 2 weeks prior to the study, (5) inability to coherently communicate with the interviewer, or (6) inability or unwillingness to give consent for participation.
Patient involvement in the study was voluntary, and patients could withdraw from the study at any time without prejudice or penalty. Patient consent to participate in the study was obtained by the investigators in writing after the patients received a thorough presentation outlining the premise of the study, including risks and benefits, as well as assurance that confidentiality would be maintained. Upon request, a copy of the consent form and a description of the study were provided to the patient. Only researchers identified in the institutional review board proposal had full access to the data, and all researchers completed a National Institutes of Health human subjects training program. The study procedures were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Touro University Institutional Review Board (Vallejo, California).
Patients with physician orders for trazodone and quetiapine for insomnia/sleep were flagged by the pharmacy staff at St Helena Hospital Center for Behavioral Health. Study investigators evaluated patient appropriateness for the study on the basis of the inclusion and exclusion criteria listed above. Figure 1 represents the patient selection process and study methodology.
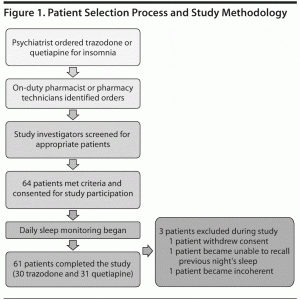
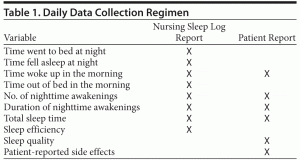
Baseline demographic data collected included age, gender, race, number of previous hospitalizations, and baseline Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) score. Subjective patient-reported data, including total sleep time, nighttime awakenings (number and duration), sleep quality (utilizing 1–4 Likert scale), and patient-reported side effects, were collected from patients each morning after ingestion of either trazodone or quetiapine (Table 1). The sleep quality question using a Likert scale was adapted from the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), which assesses past month’s sleep.29 The sleep quality question was rephrased to the patients as “How would you rate the quality of last night’s sleep?” Patients could then pick from the following scale: 1 = very bad, 2 = fairly bad, 3 = fairly good, and 4 = very good. Changes in weight were also tracked for each patient on a weekly basis during hospitalization. Objective measures of total sleep time, nighttime awakenings (number and duration), and sleep latency were collected from nursing sleep logs on a daily basis. Nurses recorded these times in 15- to 30-minute increments as part of their nocturnal shift duties. Sleep efficiency (total sleep time divided by the time in bed) was calculated using the nursing sleep logs. Dose of trazodone or quetiapine (mg per night), psychiatric diagnosis at discharge, and number of concomitant sedating medications taken at bedtime were also collected for each patient.
All statistical analyses were conducted using STATA for Windows 9.1 (Stata Corp LP, College Station, Texas). Means, standard deviations, and medians are reported for continuous data, and frequency and percentages are reported for categorical data. Pearson χ2 test was used for categorical variables. A 2-sample t test with equal variance was used for continuous variables. Wilcoxon rank sum test (Mann-Whitney) was used for sleep quality rankings.
RESULTS
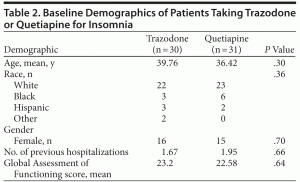
A total of 30 trazodone patients (132 study nights) and 31 quetiapine patients (180 study nights) were included in the study. As shown in Table 2, baseline demographics including age, race, gender, number of previous hospitalizations, and GAF score were similar between the 2 study groups. The mean nightly dose of trazodone and quetiapine was 102 mg (range, 12.5 mg–300 mg) and 182 mg (range, 12.5 mg–1,500 mg), respectively. The median dose of trazodone and quetiapine used by patients in this study was 100 mg per night. Patients receiving quetiapine were on a greater mean number of sedating psychotropic agents at bedtime than those receiving trazodone (2.79 vs 1.93, respectively, P < .01). Diagnoses at discharge were similar with the exception that there were more patients diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder in the quetiapine group (P < .05).
For study nights when values were unobtainable due to either missing patient interview for subjective data or missing nursing records, statistical analyses were conducted in 2 distinct ways and the results were compared. The results were analyzed using the last observation carried forward method and repeated again with the missing values dropped from the study. For all study parameters except total sleep time from nursing logs and sleep quality, both analyses produce concordant results. Results reported in this article are those found through the analysis with missing values dropped.
As presented in Table 3, patients receiving trazodone reported greater mean ± SD hours of total sleep time than those receiving quetiapine (7.80 ± 2.21 vs 6.75 ± 2.84, P < .01). This finding was replicated by calculation of total sleep time from nursing sleep logs (9.13 ± 1.52 vs 8.68 ± 2.03, P = .04). The nursing sleep log results indicated fewer mean number of nighttime awakenings for patients receiving trazodone compared to quetiapine (0.52 vs 0.75, respectively, P = .04). The 2 groups did not differ in sleep efficiency, sleep latency, sleep quality, and number of nighttime awakenings reported by patients.
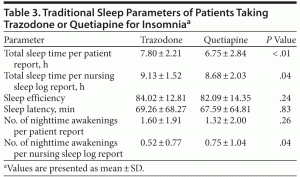
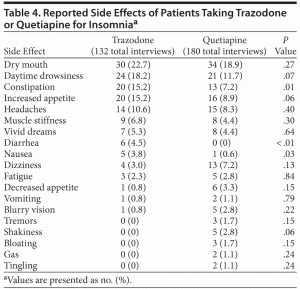
Table 4 provides the patient-reported side effects. Patients receiving trazodone reported more days of gastrointestinal side effects compared to those receiving quetiapine: constipation (17.7% vs 8.0%, respectively, P < .02), nausea (4.4% vs 0.6%, respectively, P < .05), and diarrhea (5.31% vs 0%, respectively, P < .01).
DISCUSSION
On the basis of our findings, in the inpatient psychiatric setting, trazodone may be a more appropriate first-line agent than quetiapine to treat insomnia, given the improvement found in patient-reported total sleep time by around 1 hour, increasing nurse-recorded total sleep time, and decreasing the number of nighttime awakenings in patients. Of interest, a study of trazodone in patients with depression showed objective benefits in sleep, including increases in sleep efficiency, total sleep time, total sleep period, NREM stage 3 sleep, and REM duration, as well as decreases in wakefulness during the total sleep period, early morning awakening, and S2.30 Although not detected in our study, subjective improvements in sleep, including improvement in subjective sleep quality, affectivity, and somatic complaints, have also been seen with the use of trazodone in depressed patients. In other primary insomnia studies, quetiapine has been shown to increase total sleep time and decrease sleep latency.31,32 In our study, as compared to trazodone, no changes in sleep latency were observed.
Similar to other hospital formularies, at this time, trazodone is less costly than quetiapine at the Center for Behavioral Health. For the median generic medication doses considered in this study (100 mg), quetiapine costs approximately 5 times as much as trazodone, which may pose a considerable hardship on patients with regard to affordability once the patient is discharged.
This study was not without limitations. Primarily, this was an observational study and not a randomized controlled trial. While the baseline characteristics, including number of previous hospitalizations and GAF scores, were similar between the 2 groups, patients in the quetiapine group received a greater number of sedating medications at bedtime and showed a trend toward longer lengths of hospitalization (8.5 days vs 12.1 days, P = .06), suggesting more severe psychiatric illness in this group. The difference in severity may have contributed to differences in sleep parameters.
Additionally, the inpatient stay allows for more support and structured care for the patients. A study of Veterans Affairs patients attending a partial hospitalization program suggested that the structure of the program helped with improvements in sleep parameters.33 Inpatient hospitalization could lead to improvement in psychiatric condition and, in turn, improvements in sleep. Therefore, more studies are needed in various settings to confirm the effects of trazodone and quetiapine.
Another weakness of the study is that neither polysomnography nor actigraphy were used to obtain objective data. Objective data were based on nursing records of sleep determined by night shift nurses who varied from night to night, not standardized polysomnographic readings. This factor may have decreased consistency and introduced differences in nursing log tabulations. Along the same lines, subjective data relied on the patients’ ability to recall the previous night’s sleep.
In addition, this study was powered to detect difference in traditional sleep parameters but not in patient-reported side effects or length of hospitalization. We should be mindful that the findings of this study may not be generalizable to all psychiatric settings and psychiatric patients.
In particular circumstances, the patient may benefit from a trial of quetiapine before trazodone. As an antidepressant at higher doses, trazodone is a better option for patients with depressive disorders, whereas quetiapine can be used as an adjunct for depression and also has mood-stabilizing properties, making it a better option for bipolar disorder than trazodone.20 In our patient population, the diagnoses at discharge did not differ for the most part, although there tended to be more patients with schizoaffective disorder in the quetiapine group. The schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder diagnoses are not well differentiated in the DSM-IV-TR, which was in use when this study took place.34 In order for patients to meet diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder, they must first meet criteria for schizophrenia.34 In the clinical setting, a major portion of patients with schizophrenia and mood symptoms may receive a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder.35,36 Since the 2 diagnoses are not well differentiated in the clinical setting, we also looked at combining diagnoses of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder in 1 group. When patients with diagnoses of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder were combined in the analysis, there were no differences in diagnoses between the 2 groups (P = .15). In the recently published DSM-5, schizoaffective disorder diagnostic criteria include that mood disorder episodes have been present for the majority of the total active and residual course of illness, from the onset of psychotic symptoms up until the current diagnosis.37,38 As a result, this change in diagnostic criteria poses a clearer separation between schizophrenia with mood symptoms and schizoaffective disorder, hopefully decreasing misdiagnosis.37
Additionally, differences in the side-effect profile should be considered when deciding on the appropriate first-line sleep agent in the psychiatric setting. Our findings show that patients taking trazodone may experience gastrointestinal patient-reported side effects at a higher rate than those taking quetiapine. Therefore, if the patient is unable to tolerate trazodone due to immediate side effects, quetiapine may be a better alternative.
Although minor gastrointestinal adverse effects were more common with trazodone than quetiapine, we should be aware of the potential significant metabolic side effects such as weight gain, glucose disturbances, and hyperlipidemia that may manifest with quetiapine use long-term.39,40 Second-generation antipsychotics have also been shown to increase mortality in patients with dementia.41 In this study, there was a trend toward greater weight gain in patients receiving quetiapine compared to trazodone (3.65 kg vs −1.45 kg, respectively, P = .08) at the 2-week hospitalization time point. In the inpatient psychiatric setting, where the average length of stay ranges from 7 to 14 days, the side-effect profile for these agents may not be accurately captured. The short durations of hospitalization may allow enough time to detect a significantly higher incidence of gastrointestinal patient-reported side effects with trazodone, but not enough time to detect a significant difference in metabolic side effects of quetiapine use that occur gradually with long-term use of the medication. Also, gastrointestinal side effects with trazodone are usually transient, lasting 1 to 2 weeks. The usual common side effects with trazodone include somnolence, headache, dizziness, and dry mouth and, rarely, corrected QT prolongation, priapism, and suicidal ideation.42 In this study, no differences in these side effects were observed between the 2 groups. In clinical studies, it has been shown that quetiapine is associated with a 1% to 2% incidence of restless leg syndrome, and trazodone has rare reports of akathisa.43–45 It should also be noted that antidepressants and antipsychotics can trigger restless leg symptoms, and periodic limb movements can result in nighttime awakenings, thereby worsening insomnia.46
Current studies have attempted to identify reasons that providers use second-generation antipsychotic agents rather than safer and less-costly alternatives; more studies in this area are needed.47 The use of polysomnography is difficult in the inpatient setting, but may aid in better understanding fine differences between these agents. Several studies suggest that trazodone improves insomnia in patients who do not have psychiatric diagnoses by increasing NREM stage 3 sleep, but findings with regard to its effects on the length of REM sleep vary between these studies.48–51 Additionally, a study of quetiapine in unipolar and bipolar depressed patients shows increases in total stage 2 sleep and non–REM sleep, with a decreased total sleep time in REM sleep after 2 to 4 days of treatment, but these benefits were not seen after 28 days.52
In order to maximize clinical impact and utility, studies should compare a variety of non–habit-forming agents optimally in the same setting. More head-to-head studies are needed in patients with psychiatric diagnoses and insomnia, as this population is understudied.
Drug names: diphenhydramine (Benadryl and others), eszopiclone (Lunesta), quetiapine (Seroquel), trazodone (Oleptro and others), zolpidem (Ambien, Edluar, and others).
Author affiliations: College of Pharmacy, Touro University, Vallejo, California (all authors); and School of Pharmacy, West Coast University, Los Angeles, California (Dr Chou).
Potential conflicts of interest: None reported.
Funding/support: None reported.
Previous presentations: College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists; April 22, 2013; Colorado Springs, Colorado; and Touro College of Pharmacy Research Day; April 24, 2013; Vallejo, California.
Acknowledgment: The authors thank the St Helena Hospital, Center for Behavioral Health staff for support of this project.
REFERENCES
1. Katz DA, McHorney CA. The relationship between insomnia and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic illness. J Fam Pract. 2002;51(3):229–235. PubMed
2. National Sleep Foundation. Sleep in America: 1995 Gallup poll. http://www.stanford.edu/~dement/95poll.html. Updated February 12, 1999. Accessed August 21, 2013.
3. Culpepper L. Secondary insomnia in the primary care setting: review of diagnosis, treatment, and management. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22(7):1257–1268. doi:10.1185/030079906X112589 PubMed
4. Shochat T, Umphress J, Israel AG, et al. Insomnia in primary care patients. Sleep. 1999;22(suppl 2):S359–S365. PubMed
5. Mellinger GD, Balter MB, Uhlenhuth EH. Insomnia and its treatment: prevalence and correlates. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985;42(3):225–232. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790260019002 PubMed
6. Bixler EO, Kales A, Soldatos CR, et al. Prevalence of sleep disorders in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. Am J Psychiatry. 1979;136(10):1257–1262. PubMed
7. Chevalier H, Los F, Boichut D, et al. Evaluation of severe insomnia in the general population: results of a European multinational survey. J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(suppl 1):S21–S24. PubMed
8. Hohagen F, Rink K, Käppler C, et al. Prevalence and treatment of insomnia in general practice: a longitudinal study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1993;242(6):329–336. doi:10.1007/BF02190245 PubMed
9. Vollrath M, Wicki W, Angst J. The Zurich Study, 8, insomnia: association with depression, anxiety, somatic syndromes, and course of insomnia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci. 1989;239(2):113–124. doi:10.1007/BF01759584 PubMed
10. Zeitlhofer J, Rieder A, Kapfhammer G, et al. Epidemiology of sleep disorders in Austria. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1994;106(3):86–88. PubMed
11. Passarella S, Duong MT. Diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(10):927–934. doi:10.2146/ajhp060640 PubMed
12. Weyerer S, Dilling H. Prevalence and treatment of insomnia in the community: results from the Upper Bavarian Field Study. Sleep. 1991;14(5):392–398. PubMed
13. Becker PM. Treatment of sleep dysfunction and psychiatric disorders. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2006;8(5):367–375. doi:10.1007/s11940-006-0026-6 PubMed
14. Hajak G, Müller WE, Wittchen HU, et al. Abuse and dependence potential for the non-benzodiazepine hypnotics zolpidem and zopiclone: a review of case reports and epidemiological data. Addiction. 2003;98(10):1371–1378. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2003.00491.x PubMed
15. Smith MT, Perlis ML, Park A, et al. Comparative meta-analysis of pharmacotherapy and behavior therapy for persistent insomnia. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159(1):5–11. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.159.1.5 PubMed
16. Passaro A, Volpato S, Romagnoni F, et al. Benzodiazepines with different half-life and falling in a hospitalized population: the GIFA Study. Gruppo Italiano di Farmacovigilanza nell’Anziano. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53(12):1222–1229. doi:10.1016/S0895-4356(00)00254-7 PubMed
17. Hemmelgarn B, Suissa S, Huang A, et al. Benzodiazepine use and the risk of motor vehicle crash in the elderly. JAMA. 1997;278(1):27–31. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03550010041037 PubMed
18. Hurlbut KM. Drug-induced psychoses. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1991;9(1):31–52. PubMed
19. Haria M, Fitton A, McTavish D. Trazodone: a review of its pharmacology, therapeutic use in depression and therapeutic potential in other disorders. Drugs Aging. 1994;4(4):331–355. doi:10.2165/00002512-199404040-00006 PubMed
20. Mendelson WB. A review of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of trazodone in insomnia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(4):469–476. doi:10.4088/JCP.v66n0409 PubMed
21. Nemeroff CB, Kinkead B, Goldstein J. Quetiapine: preclinical studies, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, and dosing. J Clin Psychiatry. 2002;63(suppl 13):5–11. PubMed
22. Tsuno N, Besset A, Ritchie K. Sleep and depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(10):1254–1269. doi:10.4088/JCP.v66n1008 PubMed
23. Thase ME. Depression and sleep: pathophysiology and treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2006;8(2):217–226. PubMed
24. Caldwell DF, Domino EF. Electroencephalographic and eye movement patterns during sleep in chronic schizophrenic patients. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1967;22(5):414–420. doi:10.1016/0013-4694(67)90168-X PubMed
25. Zarcone VP Jr, Benson KL, Berger PA. Abnormal rapid eye movement latencies in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987;44(1):45–48. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800130047007 PubMed
26. Lauer CJ, Schreiber W, Pollmächer T, et al. Sleep in schizophrenia: a polysomnographic study on drug-naive patients. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1997;16(1):51–60. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(96)00159-5 PubMed
27. Bench CJ, Friston KJ, Brown RG, et al. The anatomy of melancholia: focal abnormalities of cerebral blood flow in major depression. Psychol Med. 1992;22(3):607–615. doi:10.1017/S003329170003806X PubMed
28. Keshavan MS, Reynolds CF 3rd, Miewald MJ, et al. Delta sleep deficits in schizophrenia: evidence from automated analyses of sleep data. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(5):443–448. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.55.5.443 PubMed
29. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, et al. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989;28(2):193–213. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4 PubMed
30. Saletu-Zyhlarz GM, Abu-Bakr MH, Anderer P, et al. Insomnia in depression: differences in objective and subjective sleep and awakening quality to normal controls and acute effects of trazodone. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2002;26(2):249–260. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(01)00262-7 PubMed
31. Tassniyom K, Paholpak S, Tassniyom S, et al. Quetiapine for primary insomnia: a double blind, randomized controlled trial. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010;93(6):729–734. PubMed
32. Wiegand MH, Landry F, Brückner T, et al. Quetiapine in primary insomnia: a pilot study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;196(2):337–338. doi:10.1007/s00213-007-0968-8 PubMed
33. Khawaja IS, Dieperink ME, Thuras P, et al. Effect of sleep skills education on sleep quality in patients attending a psychiatry partial hospitalization program. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2013;15(1). PubMed
34. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
35. Kane JM. Strategies for making an accurate differential diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(suppl 2):4–7. doi:10.4088/JCP.9096su1cc.01 PubMed
36. Brambilla P, Barale F, Caverzasi E, et al. Clozapine-treated subjects with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a systematic review of experimental and observational studies. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2002;17(4):189–195. doi:10.1097/00004850-200207000-00006 PubMed
37. Malaspina D, Owen MJ, Heckers S, et al. Schizoaffective disorder in the DSM-5 [published online ahead of print May 23, 2013]. Schizophr Res. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.04.026 PubMed
38. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
39. Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, et al. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156(11):1686–1696. PubMed
40. Williams SG, Alinejad NA, Williams JA, et al. Statistically significant increase in weight caused by low-dose quetiapine. Pharmacotherapy. 2010;30(10):1011–1015. doi:10.1592/phco.30.10.1011 PubMed
41. Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Insel P. Risk of death with atypical antipsychotic drug treatment for dementia: meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA. 2005;294(15):1934–1943. doi:10.1001/jama.294.15.1934 PubMed
42. Fagiolini A, Comandini A, Catena Dell’Osso M, et al. Rediscovering trazodone for the treatment of major depressive disorder. CNS Drugs. 2012;26(12):1033–1049. doi:10.1007/s40263-012-0010-5 PubMed
43. Seroquel (quetiapine fumarate) [package insert]. Wilmington, DE: AstraZeneca; 2013. http://www1.astrazeneca-us.com/pi/seroquel.pdf. Accessed September 13, 2013.
44. Seroquel XR. (quetiapine fumarate extended-release tablets) [package insert]. Wilmington, DE: AstraZeneca; 2013. http://www1.astrazeneca-us.com/pi/seroquelxr.pdf. Accessed September 13, 2013.
45. Desyrel (trazodone) tablets [package insert]. Morgantown, WV: Bristol-Myers Squibb; 2005. http://www.psych.uic.edu/csp/physicians/Patient%20package%20inserts/Desyrel.pdf. Accessed September 13, 2013.
46. Hornyak M, Feige B, Voderholzer U, et al. Polysomnography findings in patients with restless legs syndrome and in healthy controls: a comparative observational study. Sleep. 2007;30(7):861–865. PubMed
47. Hermes ED, Sernyak M, Rosenheck R. Use of second-generation antipsychotic agents for sleep and sedation: a provider survey. Sleep. 2013;36(4):597–600. PubMed
48. Suzuki H, Yamadera H, Nakamura S, et al. Effects of trazodone and imipramine on the biological rhythm: an analysis of sleep EEG and body core temperature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2002;69(4):333–341. doi:10.1272/jnms.69.333 PubMed
49. Anderson IM, Sarsfield A, Haddad PM. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of quetiapine augmentation in treatment resistant depression: an open-label, pilot study. J Affect Disord. 2009;117(1-2):116–119. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2008.12.016 PubMed
50. Montgomery I, Oswald I, Morgan K, et al. Trazodone enhances sleep in subjective quality but not in objective duration. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;16(2):139–144. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb04977.x PubMed
51. Roth AJ, McCall WV, Liguori A. Cognitive, psychomotor and polysomnographic effects of trazodone in primary insomniacs. J Sleep Res. 2011;20(4):552–558. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2869.2011.00928.x PubMed
52. Gedge L, Lazowski L, Murray D, et al. Effects of quetiapine on sleep architecture in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2010;6:501–508. PubMed
Please sign in or purchase this PDF for $40.00.
Save
Cite
