ABSTRACT
Objective: To provide an overview of the role of umbilical cord blood (UCB) in managing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) symptoms in children aged 4–8 years.
Data Sources: A systematic literature search was conducted using the terms (autism OR autism spectrum disorder AND umbilical cord blood infusion UCB OR umbilical cord blood). The review was limited to articles published in the English language from 1945 to September 2020. The database search included PubMed, Scopus, and EMBASE.
Study Selection: The initial search revealed 165 hits of potential relevance.
Data Extraction: The articles were analyzed to obtain clinical information relevant to meeting the review objectives.
Data Synthesis: After title, abstract, and full article review, 3 UCB studies were selected for analysis.
Results: The systematic review showed mixed results. In the first study, improvements were seen in the socialization and communication domains and adaptive behavior with UCB infusion. The Pervasive Developmental Disorder Behavior Inventory composite T score and Expressive One-Word Picture Vocabulary Test (EOWPVT) score also improved. Symptomatic improvement was seen in half of the patients. The second study showed no improvement in the EOWPVT, Receptive One-Word Picture Vocabulary Test, Clinical Global Impressions scale, or Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales (VABS), second edition. The third study showed nonsignificant improvement in the VABS, third edition socialization scale scores; however, major improvement in the communication domain was seen for those with nonverbal IQ ≥ 70. No serious adverse events were reported in any of the studies.
Conclusion: Few studies have evaluated the role of UCB infusion in addressing symptoms of ASD. Due to the limited number of studies, more research is warranted.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2022;24(3):21r03042
To cite: Adnan M, Motiwala F, Trivedi C, et al. Human umbilical cord blood infusions in the management of autism spectrum disorder. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2022;24(3):21r03042.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.21r03042
© Copyright 2022 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aDepartment of Psychiatry, Center for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
bDepartment of Psychiatry, Texas Tech University Health Science Center at Permian Basin, Midland, Texas
cDepartment of Psychiatry, Boston Children’s Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts
*Corresponding author: Mahwish Adnan, MD, Center for Addiction and Mental Health, 1000 Queen St W, Toronto, Ontario M6J 1H4, Canada ([email protected]).
One in 54 US children is diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).1 ASD presents with abnormalities in social interaction, impaired verbal and nonverbal communication, and repetitive behavior, with a broad spectrum of severity from mild to disabling. The lifetime expense supporting a person with ASD without an intellectual disability is estimated to be $1.4 million compared to $2.4 million for people with comorbid intellectual disabilities.2 In 2017, a study3 found total annual health care expenditures for ASD to be $13,700 versus $8,560 for non-ASD patients. The symptoms of ASD are usually noted by caregivers by 12–18 months of age.4 The conclusive ASD diagnosis usually occurs around age 24–36 months; however, the diagnosis might be delayed until adulthood in some mild severity cases.5
Standard of care for ASD encompasses a combination of behavioral, nutritional, and pharmacologic interventions. There is sparse evidence to support the efficacy of nutritional intervention for ASD symptom management. Pharmacologic interventions include psychostimulants for comorbid attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for associated anxiety and depression, and atypical antipsychotics (aripiprazole, risperidone, and off-label olanzapine) for aggression and self-injurious behavior.6–8 The side effect profile of the pharmacologic interventions is concerning. Behavioral interventions typically include activities designed to promote social interaction and communication. However, even the combination of pharmacologic and behavioral interventions cannot influence core ASD psychopathology.9 Recent trials with umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal and stromal cell transplantation10 and umbilical cord blood (UCB) infusion11–15 in the management of ASD have shown promise.
Umbilical Cord Blood Pharmacology and Mechanism of Action
UCB-based stem cells retrieved at birth have expanded the horizons of medical interventions. The UCB pluripotent stem cells on infusion relocate to the bone marrow and lymphatic regions. These stem cells can breach the blood-brain barrier and appear to gather near injury sites and other central nervous system regions containing endogenous stem cell populations. The infused cells stimulate endogenous stem cells.16 Currently, the exact mechanisms in humans are poorly understood.17
The exact pathophysiology of ASD is uncertain. The proposed causes include overactive immune system,18 white matter abnormalities,19 brain synaptic irregularities,20,21 neuroinflammation,22 presence of maternal antibodies in fetal brain tissue,23 unusual levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) in the cerebrospinal fluid,24 or abnormal microglial activation, leading to excessive aberrant neural connectivity pathways.25,26 ASD therapy with UCB promotes neural cell protection and repair, reducing inflammation.27 Cord blood stem cells respond through paracrine signaling to modulate brain inflammation and immune abnormalities,27 enhancing socialization, communication, and adaptive behavior.27–29 Infusions of autologous cord blood cells are safe and beneficial with other brain injuries such as cerebral palsy, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, and congenital hydrocephalus.30–32
METHODS
Our search strategy and data extraction followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.33 A systematic literature search was conducted independently by 2 contributing authors (M.A. and C.T.) using (autism OR autism spectrum disorder AND umbilical cord blood infusion UCB OR umbilical cord blood) in PubMed, Scopus, and EMBASE. The review was limited to articles published in the English language from 1945 to September 2020. Citations and references were reviewed from all included studies to identify additional potential studies. The authors read the full articles for relevance and pertinence. The third reviewer (F.M.) resolved any conflict that arose about the inclusion of any study in this review. Also, we checked for ongoing studies at the National Institutes of Health clinical trials and National Library of Medicine (ClinicalTrials.gov). Data were extracted based on the following inclusion criteria: (1) studies published in English, (2) human studies, (3) participants aged ≥ 18 years, (4) participants with a primary diagnosis of ASD based on DSM-IV/V criteria, (5) studies focused on utilization of UCB infusions as an intervention, and (6) study designs: open-label and randomized controlled trials. Previously published systematic reviews, case series, case reports, opinions, comments, editorials, and unpublished studies were excluded. The 3 studies included in the analysis displayed heterogeneous data; hence, meta-analysis is not possible. Thus, a systematic review was performed.
RESULTS
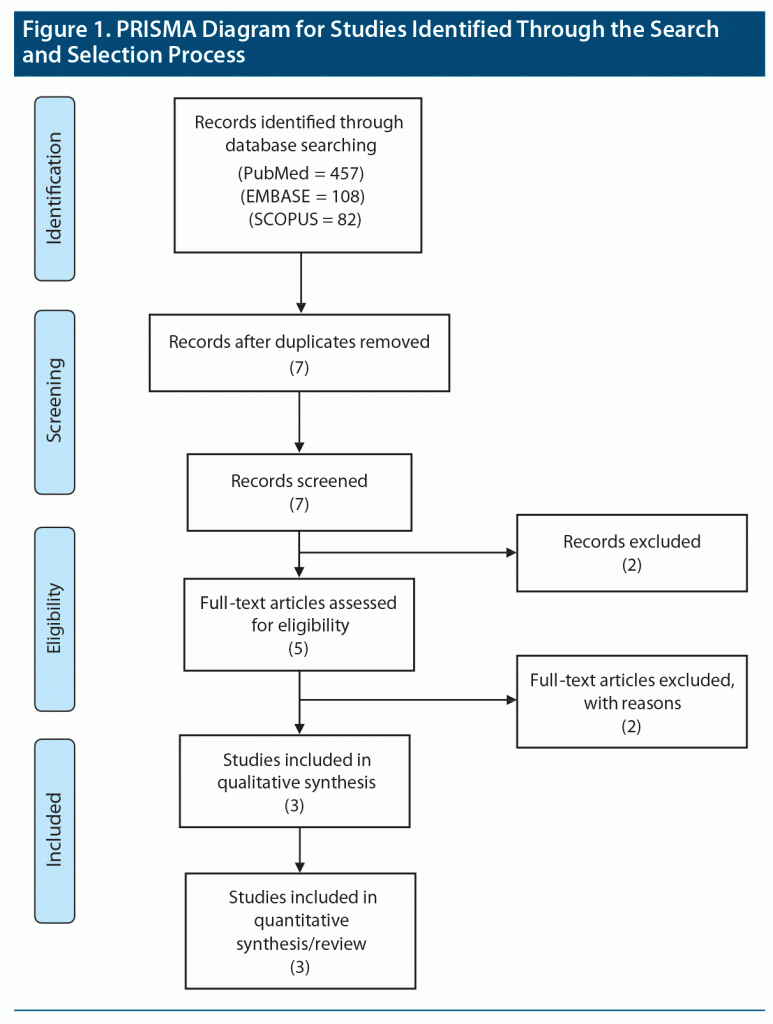
The initial literature search resulted in 165 hits. After the title and abstract review and removing all duplicates, we retrieved 7 relevant articles. After the full-text review, we excluded 4 articles based on our inclusion criteria and extracted data from 3 articles (Figure 1).11–13 Table 1 provides the study characteristics.
Efficacy Outcome
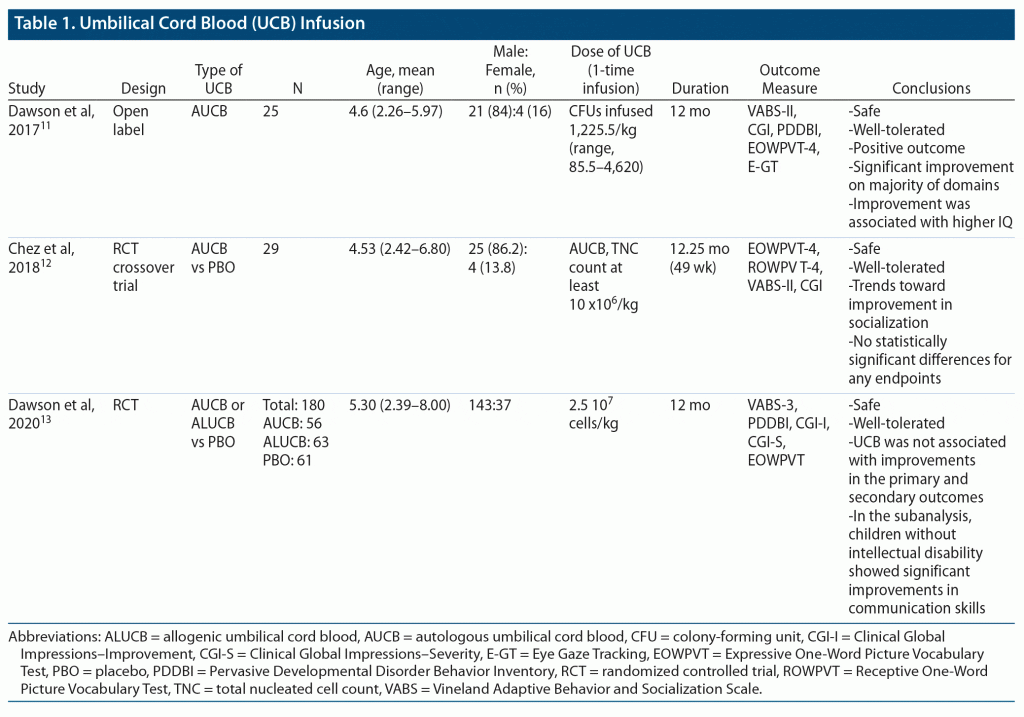
A single-center, open-label trial by Dawson et al11 evaluated the safety and feasibility of autologous cord blood transfusion in 25 children (median age of 4.6 years). The primary outcome was adaptive behavior. The Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, second edition (VABS-II) was used to evaluate adaptive behavior, which showed 3-point improvement at 6 months (P = .007). In the separate analysis of the VABS-II domain, socialization and communication scores showed a 2-point and 4.5-point improvement (P < .05) at 6 months. There was no improvement in the motor and daily living skills domain. There was a correlation between nonverbal IQ score and improvement in socialization domain (r = 0.57) and adaptive behavior domain (r = 0.42) scores in the subanalysis. Patients with higher nonverbal IQ scores showed more improvement than others. There was no correlation between change in the communication domain score and nonverbal IQ score (r = 0.22). Scores of each domain or composite score showed no change from 6 to 12 months. The Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) scale evaluated autism symptom severity at baseline and change in severity with intervention. At baseline, 73% of patients had moderately severe to very severe symptoms, which improved to 45% of patients at 6 months. There was more than minimal symptomatic improvement in 50% of patients at 6 months and 45% of patients at 12 months. Parents noted symptomatic improvement as measured by the composite T score of the Pervasive Developmental Disorder Behavior Inventory (PDDBI) (median improvement: 7.5, P = .004). From 6 months to 12 months, there was no change in the score. The Expressive One-Word Picture Vocabulary Test (EOWPVT) score, which reflects the ability to name a picture, showed improvement in 57% of patients at 6 months (P = .001) and 68% (P = .001) at 12 months.11
Chez et al12 analyzed safety and efficacy in 29 children (aged 2–6 years) in a placebo-controlled crossover randomized trial. The primary outcome was the ability to name the picture (EOWPVT-4 and Receptive One-Word Picture Vocabulary Test [ROWPVT-4]). The baseline mean EOWPVT score was low in the UCB group (mean score: 63) compared to placebo (mean score: 82). Fluid reasoning and knowledge assessment by Stanford-Binet Fluid Reasoning and Knowledge did not show significant change at follow-up. For the VABS-II subscale, the socialization domain showed improvement (baseline: 69, 12 weeks: 75, 24 weeks: 77) in the UCB group. However, the score remained the same in the placebo group (baseline: 72, 12 weeks: 70, follow-up: 72), and the difference was not statistically significant.12 There was no change in scores in the other domains (communication, motor, daily, adaptive behavior). Almost half the patients after 12 weeks showed CGI scale improvement in both the placebo and UCB groups.12
The third study conducted by Dawson et al13 was a placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial on the safety and efficacy of UCB infusion for treating children with ASD. The primary outcome was change in the VABS-III socialization standard score. Of 180 patients, 56 received autologous UCB infusion, 63 received allogeneic UCB infusion, and 61 received a placebo. After 6 months, the VABS-III socialization standard subscore was more improved in the UCB group (3.13 vs 1.98), but there was no significant difference compared to the placebo group (P = .46). There was no difference in the VABS-III socialization standard subscore between autologous or allogeneic UCB infusion groups. Children without intellectual disability (nonverbal IQ ≥ 70) showed a better response in the communication domain of the VABS-III standard score.13 With 6 months of UCB treatment among patients with nonverbal IQ ≥ 70, the communication domain score was 5.45 times higher than those for the non-UCB group. For the CGI, half of the patients in all 3 groups showed symptom improvement. However, in patients with nonverbal IQ ≥ 70, more improvement was observed in the UCB group than in the placebo group (65.9% vs 57.1%).13 Table 2 provides an overview of the scales of improvement for the 3 studies.
Safety Outcome
The open-label trial by Dawson et al11 showed no severe side effects. Treatment-related side effects occurred in 13% of patients (allergic reactions: urticaria, cough). Unrelated to infusion, typical side effects were agitation, skin changes, and infections.
There were no severe side effects in the randomized study by Chez et al.12 The mild to moderate side effects included constitutional disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and pulmonary disorders. Of 86 side effects in 29 patients, 80% were unrelated to CB transfusion. Only 3% (renal disorders, constitutional symptoms) were probably due to UCB infusion, and 16% of side effects (mainly gastrointestinal disorders) were possibly due to infusion. None of the adverse events required treatment.
Finally, in the randomized study by Dawson et al,13 5.3% of patients in the placebo and 2.5% in the UCB group had severe adverse events unrelated to treatment. No severe side effects were related to treatment. Mild infusion-related reactions occurred in 6.6% of patients in the placebo group and 4.2% of patients in the UCB group (P = .72). In 5.9% of patients, moderate to severe infusion reactions occurred among the UCB group. All severe infusion reactions (bronchospasm, facial flushing, swelling) occurred in allogeneic UCB groups only. The frequency of infusion reactions was higher in the allogeneic group than in the autologous group but was not statistically significant (14.3% vs 5.4%, P = .10).
DISCUSSION
UCB infusion offers a new dimension to the management of ASD. The available literature indicates that UCB infusion can be a safe and tolerable approach to ASD symptom management. The improvements in socialization domains, particularly in higher nonverbal IQ ASD patients, were associated with significant behavioral improvements.
The efficacy of UCB is also evident by observing the correlation of the changes in the electroencephalography (EEG), white matter tract, and electrophysiologic biomarkers with clinical improvement. UCB infusion changes to the white matter tract are detectable by diffusion-weighted images at baseline and 6 months after a single infusion. Such an increase in white matter connectivity in frontal, temporal, and subcortical regions (hippocampus and basal ganglia) is associated with better behavioral and social communication skills and reduced symptoms of ASD.14 Additionally, significant EEG changes are noticeable at 12 months post infusion, characterized by increased α and β power and decreased EEG theta power. Higher baseline posterior EEG β power is associated with a significant improvement in social communication symptoms.15 UCB infusion has shown promise in childhood hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and congenital hydrocephalus.30,31 The UCB intervention combined with erythropoietin in children with cerebral palsy improves motor and cognitive impairment and the neural circuitry’s metabolic and structural changes.32
The strength of our review includes the stringent inclusion criteria for selecting only those studies with the most robust and scientific design. A limited number of heterogeneously designed studies with small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and less standardized control groups limit our findings and conclusion. All the studies included in our analysis were conducted at the Duke Center for Autism and Brain Development. The participants in these studies were from a single demographic area, which limits generalizability. The uncontrolled open-label study11 limited our determination if the observed behavioral changes were due to the treatment or reflected the preschool period’s natural course.34 The findings of the 2017 study11 were limited because of the lack of blinding and control groups. However, the crossover design used by Chez et al12 resulted in excellent compliance by parents for all endpoints. The significant limitation of that study12 was the challenging language assessment in the young age group and the lack of standardization of allogenic UCB dose. Although the study12 had no carryover effect for the 2 primary endpoints, the carryover effects were observed for secondary endpoints, leading to less variability between subjects. The 2020 randomized, placebo-controlled study13 was challenged due to the high expectancy effect in the placebo arm and the larger-than-anticipated number of participants with intellectual disability, which might have compromised the study results. Future studies must consider a transparent primary endpoint selection, which will need to examine the influence of cognitive ability, substantial variability among participants in clinical change over time, and expectancy effects.
CONCLUSIONS
The present study highlights the safety and tolerability of allogenic UCB infusion in children with ASD with marginal efficacy in behavioral and language outcomes. Thus, the current trials did not support the clinical use of UCB for the management of ASD. However, the evidence is from a limited number of heterogeneous clinical trials and strongly suggests its possible efficacy in the management of ASD. Therefore, future global large-scale randomized controlled trials are required to establish intervention efficacy and safety in ASD. These studies offer a glimmer of hope; however, no definitive conclusion about use of UCB in the future can be extracted. The clinical implication of UCB in treating ASD patients cannot be generalized at this time, as this area will need further studies to support its potential use.
Submitted: June 8, 2021; accepted September 17, 2021.
Published online: June 2, 2022.
Relevant financial relationships: None.
Funding/support: None.
References (34)

- Maenner MJ, Shaw KA, Baio J, et al; EdS1; PhD-7. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(4):1–12. PubMed CrossRef
- Maenner MJ, Shaw KA, Baio J, et al; EdS1; PhD-7. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(4):1–12. PubMed CrossRef
- Vohra R, Madhavan S, Sambamoorthi U. Comorbidity prevalence, healthcare utilization, and expenditures of Medicaid enrolled adults with autism spectrum disorders. Autism. 2017;21(8):995–1009. PubMed CrossRef
- Mitchell S, Brian J, Zwaigenbaum L, et al. Early language and communication development of infants later diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2006;27(suppl):S69–S78. PubMed CrossRef
- Filipek PA, Accardo PJ, Baranek GT, et al. The screening and diagnosis of autistic spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 1999;29(6):439–484. PubMed CrossRef
- McCracken JT. Safety issues with drug therapies for autism spectrum disorders. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(suppl 10):32–37. PubMed
- Tandon M, Pruett JR Jr. An overview of the use of antidepressants in children and adolescents. Mo Med. 2008;105(1):79–84, quiz 84–85. PubMed
- Nevels RM, Dehon EE, Alexander K, et al. Psychopharmacology of aggression in children and adolescents with primary neuropsychiatric disorders: a review of current and potentially promising treatment options. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2010;18(2):184–201. PubMed CrossRef
- Sharma SR, Gonda X, Tarazi FI. Autism spectrum disorder: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;190:91–104. PubMed CrossRef
- Nguyen Thanh L, Nguyen HP, Ngo MD, et al. Outcomes of bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation combined with interventional education for autism spectrum disorder. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(1):14–26. PubMed CrossRef
- Dawson G, Sun JM, Davlantis KS, et al. Autologous cord blood infusions are safe and feasible in young children with autism spectrum disorder: results of a single‐center phase I open‐label trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(5):1332–1339. PubMed CrossRef
- Chez M, Lepage C, Parise C, et al. Safety and observations from a placebo‐ controlled, crossover study to assess use of autologous umbilical cord blood stem cells to improve symptoms in children with autism. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(4):333–341. PubMed CrossRef
- Dawson G, Sun JM, Baker J, et al. A phase II randomized clinical trial of the safety and efficacy of intravenous umbilical cord blood infusion for treatment of children with autism spectrum disorder. J Pediatr. 2020;222:164–173.e5. PubMed CrossRef
- Carpenter KLH, Major S, Tallman C, et al. White matter tract changes associated with clinical improvement in an open‐label trial assessing autologous umbilical cord blood for treatment of young children with autism. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(2):138–147. PubMed CrossRef
- Murias M, Major S, Compton S, et al. Electrophysiological biomarkers predict clinical improvement in an open‐label trial assessing efficacy of autologous umbilical cord blood for treatment of autism. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(11):783–791. PubMed CrossRef
- Garbuzova-Davis S, Willing AE, Zigova T, et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood cells in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: distribution, migration, and differentiation. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003;12(3):255–270. PubMed CrossRef
- Siniscalco D, Sapone A, Cirillo A, et al. Autism spectrum disorders: is mesenchymal stem cell personalized therapy the future? J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:480289. PubMed CrossRef
- Voineagu I, Wang X, Johnston P, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of autistic brain reveals convergent molecular pathology. Nature. 2011;474(7351):380–384. PubMed CrossRef
- Wolff JJ, Gu H, Gerig G, et al; IBIS Network. Differences in white matter fiber tract development present from 6 to 24 months in infants with autism. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169(6):589–600. PubMed CrossRef
- Gao R, Penzes P. Common mechanisms of excitatory and inhibitory imbalance in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders. Curr Mol Med. 2015;15(2):146–167. PubMed CrossRef
- Volk L, Chiu SL, Sharma K, et al. Glutamate synapses in human cognitive disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015;38(1):127–149. PubMed CrossRef
- Young AMH, Chakrabarti B, Roberts D, et al. From molecules to neural morphology: understanding neuroinflammation in autism spectrum condition. Mol Autism. 2016;7(1):9. PubMed CrossRef
- Braunschweig D, Krakowiak P, Duncanson P, et al. Autism-specific maternal autoantibodies recognize critical proteins in developing brain. Transl Psychiatry. 2013;3(7):e277. PubMed CrossRef
- Vargas DL, Nascimbene C, Krishnan C, et al. Neuroglial activation and neuroinflammation in the brain of patients with autism. Ann Neurol. 2005;57(1):67–81. PubMed CrossRef
- Morgan JT, Chana G, Pardo CA, et al. Microglial activation and increased microglial density observed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in autism. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68(4):368–376. PubMed CrossRef
- Suzuki K, Sugihara G, Ouchi Y, et al. Microglial activation in young adults with autism spectrum disorder. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(1):49–58. PubMed CrossRef
- Siniscalco D, Bradstreet JJ, Sych N, et al. Perspectives on the use of stem cells for autism treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:262438. PubMed CrossRef
- Bachstetter AD, Pabon MM, Cole MJ, et al. Peripheral injection of human umbilical cord blood stimulates neurogenesis in the aged rat brain. BMC Neurosci. 2008;9(1):22. PubMed CrossRef
- Shahaduzzaman M, Golden JE, Green S, et al. A single administration of human umbilical cord blood T cells produces long-lasting effects in the aging hippocampus. Age (Dordr). 2013;35(6):2071–2087. PubMed CrossRef
- Cotten CM, Murtha AP, Goldberg RN, et al. Feasibility of autologous cord blood cells for infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2014;164(5):973–979.e1. PubMed CrossRef
- Sun JM, Grant GA, McLaughlin C, et al. Repeated autologous umbilical cord blood infusions are feasible and had no acute safety issues in young babies with congenital hydrocephalus. Pediatr Res. 2015;78(6):712–716. PubMed CrossRef
- Min K, Song J, Kang JY, et al. Umbilical cord blood therapy potentiated with erythropoietin for children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Stem Cells. 2013;31(3):581–591. PubMed CrossRef
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. PubMed CrossRef
- Kantzer AK, Fernell E, Westerlund J, et al. Young children who screen positive for autism: stability, change and “comorbidity” over two years. Res Dev Disabil. 2018;72:297–307. PubMed CrossRef
Please sign in or purchase this PDF for $40.
Save
Cite