Objective: To determine associations between the rate of physical restraint and demographic variables such as body mass index (BMI), ethnicity, sex, and age in the emergency department (ED) along with clinical variables such as various psychiatric diagnoses and medications.
Methods: This 6-month (October 1, 2016-March 30, 2017) retrospective chart review was conducted in the ED of a community hospital, which is also a teaching institution for medical students and residents but does not have access to psychiatry consultations via phone or in person. A total of 165 agitated patients were included in the study. Agitated patients who were restrained were compared to those who were not physically restrained.
Results: Of the patients, 112 (68%) were physically restrained, and those not physically restrained were included as controls (n = 53, 32%). Younger age (P = .03), lower BMI (P = .04), intoxication (P = .001), preexisting diagnosis of depression (P = .02), and antipsychotics as a home medication (P = .03) were associated with physical restraints. In the ED, administration of haloperidol and olanzapine was associated with physical restraints. Current benzodiazepine prescription (P = .001), ED administration of ketamine (P = .001), and ED administration of diazepam (P = .001) were more common in those not physically restrained.
Conclusions: Risk factors for physical restraints can be used to identify high-risk patients early, and other treatments along with behavioral and environmental modifications may then be utilized. Further research to develop protocols using nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic measures to minimize use of restraints is required.
Disparities and Variables Associated With Physical Restraint for Acute Agitation in a Nonpsychiatric Emergency Department
ABSTRACT
Objective: To determine associations between the rate of physical restraint and demographic variables such as body mass index (BMI), ethnicity, sex, and age in the emergency department (ED) along with clinical variables such as various psychiatric diagnoses and medications.
Methods: This 6-month (October 1, 2016-March 30, 2017) retrospective chart review was conducted in the ED of a community hospital, which is also a teaching institution for medical students and residents but does not have access to psychiatry consultations via phone or in person. A total of 165 agitated patients were included in the study. Agitated patients who were restrained were compared to those who were not physically restrained.
Results: Of the patients, 112 (68%) were physically restrained, and those not physically restrained were included as controls (n = 53, 32%). Younger age (P = .03), lower BMI (P = .04), intoxication (P = .001), preexisting diagnosis of depression (P = .02), and antipsychotics as a home medication (P = .03) were associated with physical restraints. In the ED, administration of haloperidol and olanzapine was associated with physical restraints. Current benzodiazepine prescription (P = .001), ED administration of ketamine (P = .001), and ED administration of diazepam (P = .001) were more common in those not physically restrained.
Conclusions: Risk factors for physical restraints can be used to identify high-risk patients early, and other treatments along with behavioral and environmental modifications may then be utilized. Further research to develop protocols using nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic measures to minimize use of restraints is required.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2019;21(6):19m02471
To cite: Khalid Z, Fana M, Payea R, et al. Disparities and variables associated with physical restraints for acute agitation in a nonpsychiatric emergency department. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2019;21(6):19m02471.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.19m02471
© Copyright 2019 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aDepartment of Psychiatry, Central Michigan University, Saginaw, Michigan
bCentral Michigan University School of Medicine, Mt Pleasant, Michigan
cDepartment of Hospital Medicine, Covenant Healthcare, Saginaw, Michigan
dDivision of Research, Case Western University, Cleveland, Ohio
*Corresponding author: Zaira Khalid, MD, 1000 Houghton Ave, Saginaw, MI 48602 ([email protected]).
Physical restraints refer to any mechanical device, material, or equipment that limit a patient’s ability to move voluntarily.1 Restraints are commonly employed in emergency departments (EDs), psychiatric inpatient facilities, and crisis centers to ensure the safety of the patient as well as the staff involved in patient care.2 The American Psychiatric Association indicates their use only when other means of control are ineffective or appropriate and to prevent serious disruption of the treatment program or significant damage to the physical environment.3
While the use of physical restraints is imperative for proper patient management in certain settings, it is equally important to acknowledge concerns regarding the legal, ethical, and psychiatric impact such use has on patients. In elderly patients, it is advised to avoid utilization of physical restraints, as a strong correlation between their use and death from strangulation or cardiac arrest, injury, or iatrogenic complications has been found.4 Death related to physical restraints has been reported numerous times in autopsy reports of German patients due to strangulation, chest compression, or head dangling.5 Concerns for overuse of physical restraints are common in not only developed countries but also developing ones as well and highlight issues regarding patient dignity and autonomy.6 A study by Kr×¼ger et al7 collected randomized data from 3,434 direct observations between October 2008 and March 2009 and found an 11.8% prevalence rate of physical restraint use.
Interestingly, physical restraints are seldom used in Norwegian hospitals. Instead, it is common practice for nurses to keep a safe distance from the patient, maintain eye contact to avoid isolation, and stay alert for sudden patient movements. In a comparative study of patients in intensive care units by Martin and Mathisen,8 39% of a sample of patients from the United States were restrained, whereas none of an equal sample size was restrained in the Norwegian hospital. Norwegian patients were more sedated and the nurse-to-patient ratios were higher than that of their US counterpart, suggesting avenues of possible amendments to current practice in the United States.8
A more recent comprehensive retrospective cohort study by Patel et al9 showed a strong correlation between patient BMI and psychotropic medication administration. Young patients taking psychotropic medications for 3-12 months between 1995 and 2010 had a steady monthly increase (ie, between 0.16 and 0.36 kg/m2) in body mass index (BMI).9 Interestingly, no study to date has examined a possible association between patient BMI and rates of physical restraint in the ED.
In the United States, mental health care disparities have existed among racial minorities for a number of years and have reportedly increased recently.1-4 It has been reported that minorities (1) have less access to mental health services, (2) are less likely to receive these services, (3) receive poorer quality of mental health care, and (4) are underrepresented in mental health research.10,11 African-American patients, for example, are more likely to be diagnosed with psychotic disorders rather than affective disorders and are more likely to receive higher doses of antipsychotics compared to their Euro-American counterparts.11,12 Consequently, here, we aim to identify variables that impact the likelihood of physical restraint in psychiatric patients, including ethnicity, sex, age, BMI, patient medicinal profile, and patient psychiatric diagnoses prior to restraint. Moreover, we evaluate the relationship between the rate of restraint and the medication used for agitation as first-line treatment of unstable patients.
METHODS
Setting
A 6-month (October 1, 2016-March 30, 2017) retrospective chart review was conducted in the ED of a community hospital, which is also a teaching institution for medical students and residents. Many EDs in the United States have a designated psychiatric emergency service (PES), which is medically managed by psychiatrists and other mental health workers. This community hospital does not have a PES or over-the-phone psychiatric consultations available, and these patients are managed completely by the ED physicians.
Data Source
The data obtained looked at 6 months of ED visits in which patients were either physically or chemically restrained for agitation or aggression. Patients who were restrained for the purpose of medical procedures such as intubations or due to law enforcement, those aged < 18 years, and those with documented cognitive impairment were excluded.
The control group included patients who were agitated but not physically restrained. These patients were identified using orders for medications that are commonly used in the ED for aggression and agitation: olanzapine, haloperidol, ziprasidone, and lorazepam. We also searched using key words of ICD-10 diagnosis that are commonly associated with restraints. These key words included intoxication, schizophrenia, psychosis, ideations, and agitation.
During the chart review, we had access to all documentation, laboratory results, and imaging recorded during routine care. We collected data regarding age, sex, ethnicity, BMI, presence of acute intoxication, psychiatric diagnosis, home psychotropic medications, and psychotropic medications that were given in the ED as well as the documented reason for restraints such as agitation, psychosis, aggression, ideations, schizophrenia, and intoxication.
The study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (Central Michigan University, Saginaw, Michigan). The need for patient consent was waived for this retrospective review since all data were anonymous and kept confidential.
Statistical Analysis

- Use of physical restraints poses health risks and is a traumatic experience for patients.
- Patients presenting to the emergency department can be identified for early intervention using risk factors for physical restraint.
The statistical analysis was done in 3 stages. In stage 1, descriptive statistics (percentages and means depending on level of measurement) were computed for all variables collected. These analyses form the basis for describing the study sample obtained from the medical records. In stage 2, univariate measures of association (χ2 and t tests) were performed to identify the variables associated with patient restraint. These variables included demographics, diagnoses, currently prescribed psychotropics, and medications administered in the ED. The final analysis was a backward stepwise logistic regression model on preexisting variables at the time of ED presentation to eliminate the redundant predictors and to identify the smallest subset of independent predictors of patient restraint. As part of this analysis, a classification table was computed to estimate the sensitivity and specificity of the final predictive model.
RESULTS
Demographics of Patient Pool
The study included a total of 165 patients; 57% were male and the majority were white (64%), followed by black (26%) and Hispanic (10%). The mean age was 44 years with an overall range of 18-94 years. The BMI range among these patients was 15-51 kg/m2 with a mean of 27 kg/m2. Twenty-eight percent were obese, and an additional 31% were overweight.
Outcomes
Of the 165 patients, 112 (68%) were physically restrained, and those not physically restrained were included as controls (n = 53, 32%). We first examined the relation between ethnicity and rate of restraint. The restraint rates were the same for white (66%) and minority patients in this sample (69%).
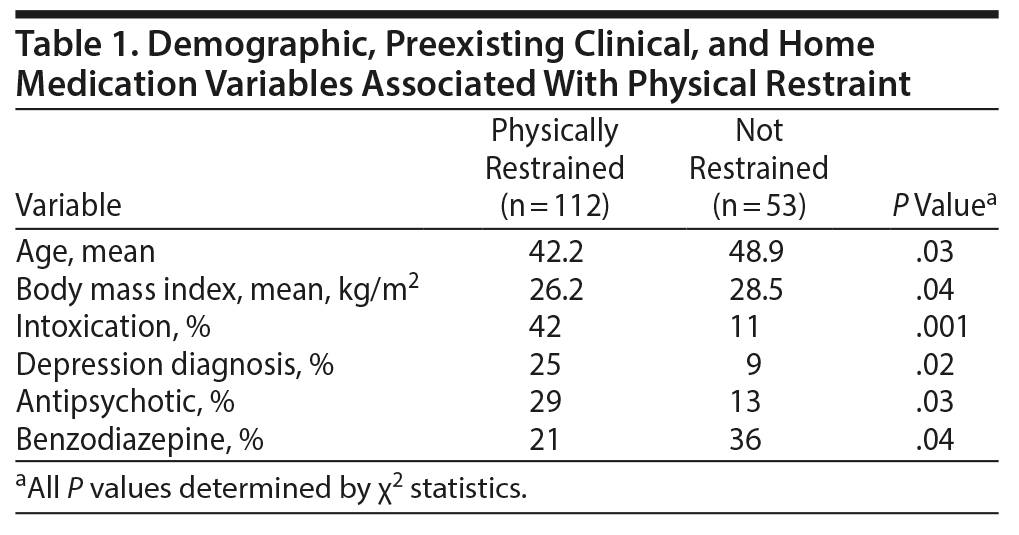
Patients who were physically restrained for agitation had a statistically significant lower mean BMI (mean = 26.2, SD = 6.6) compared to patients who were agitated but not physically restrained (mean = 28.5, SD = 6.8, t162 = 2.07, P = .04). Patients who were physically restrained were significantly younger (mean = 42, SD = 18.5) compared to patients who were not restrained (mean = 49, SD = 16.8, t163 = 2.22, P = .03) (Table 1).
Analyses were performed to compare the rates of physical restraints versus various psychiatric diagnoses and home medications (Table 1). Among patients in the restrained group, we found higher rates of acute intoxication, depression, and taking antipsychotic medications. Moreover, the number of patients taking psychiatric medications classified as "other medications" was also higher in the restrained group. Patients taking benzodiazepines at home were significantly more likely to be in the nonrestraint group.
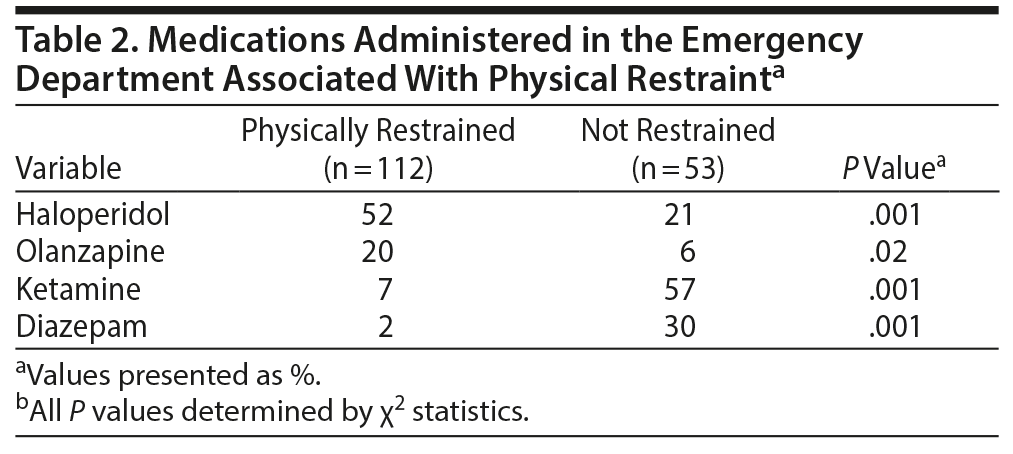
Next, we examined several psychotropic medications that were administered in the ED and their association with physical restraint (Table 2). Patients in the physically restrained group were more likely to be administered haloperidol and olanzapine, while those in the control group were more likely to be given ketamine and diazepam.
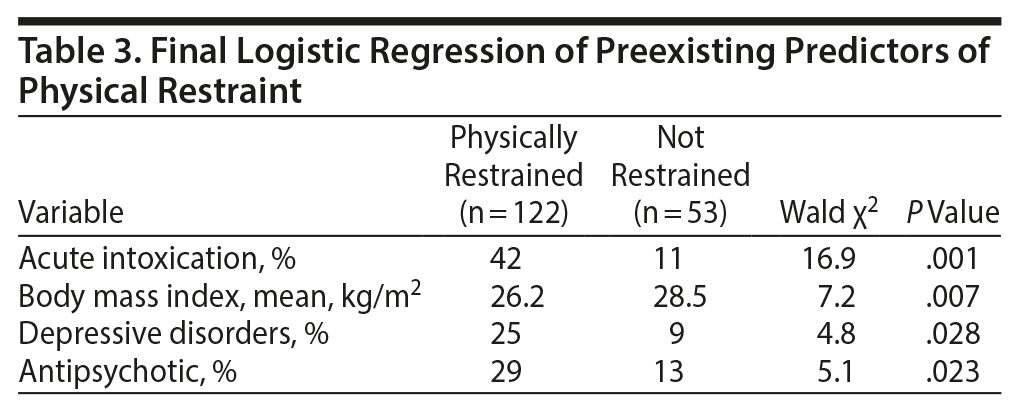
Finally, a backward elimination logistic regression analysis of the significant variables present prior to presenting to the ED, univariate predictors described previously (Table 1), resulted in 4 independent predictors of restraint (Table 3). The 4 predictors include BMI, acute intoxication, an existing diagnosis of depressive disorders, and taking antipsychotic medications. Higher percentages of patients with acute intoxication, with depressive disorder diagnosis, and taking antipsychotic medications were in the restrained group. A lower BMI also was significantly associated with being restrained.
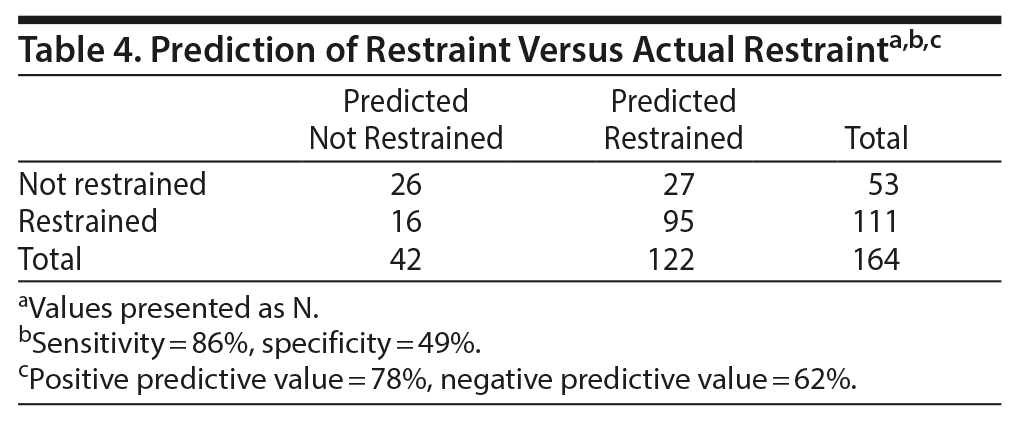
Use of these 4 independent variables to predict patient restraint resulted in the classification shown in Table 4. The resulting sensitivity was acceptable at 86%, but the specificity was much lower at 49%. The positive predictive value was 78%, and the negative predictive value was 62%. Odds ratios for the 4 predictor variables were 3.2 for depressive disorders, 2.6 for antipsychotic medication, 5.7 for acute intoxication, and 2.6 for BMI values < 25.0.
DISCUSSION
This study aimed to identify variables that could predict a higher likelihood of use of physical restraints in the ED. Disparities in ethnicity, sex, and age have been a prominent area of discussion for a number of years. Several reports4-6 have documented significantly higher incidences of physical restraint in younger populations compared to older populations. Studies13,14 have reported no significant difference between male and female rates of physical restraint in the ED, whereas others5-7 have demonstrated a significantly higher rate of physical restraint in male populations. Zun10 reported a total of 298 patients restrained in a teaching hospital ED over the course of 1 year, of whom 73% were black, 16% were Hispanic, and 11% were white.
Our results show that only age and BMI had a univariate association with restraint. A preexisting diagnosis of depression and taking multiple psychotropics also showed univariate associations with use of restraints as did acute intoxication. Moreover, 4 medications administered in the ED were associated with being restrained (Table 1 and Table 2). One limitation to interpreting these data regarding ED medications is that we do not know the order of administration between the medication and restraints. It is possible that patients who were extremely agitated required the use of both, and they were administrated simultaneously. Finally, only 4 preexisting variables remained independent predictors of physical restraint: BMI, acute intoxication, an existing diagnosis of depressive disorders, and taking antipsychotic medications. All other variables showing a univariate association with restraint were redundant and not retained in the final model.
Each of the 4 predictors could be identified upon presentation to the ED and sometimes even earlier through emergency medical service personnel. Given the high risk for physical restraint among these patients, behavioral interventions such as placing them with a sitter or removing any physical or sensory stimuli such as loud machines from their room can help reduce the rate of restraints.
The overall rate of physical restraints in this study was 63%. This high percentage raises the question of whether we are identifying these patients early enough to use other behavioral methods to deescalate the situation. As noted previously, our ED does not have a PES or over-the-phone access to psychiatrists or trained mental health professionals, and the decision to provide psychotropic medications as well as physical restraints is made by the ED physicians. When we look at other studies10,12,15 performed in Europe and the United States, the rate of restraints varied between 7% and 29%. The lack of a psychiatric ED or PES could be a large contributor to the high incidence of physical restraint in our study.
Other limitations include that the study was completed at just 1 teaching hospital with specific demographics of the population served and thus may not be generalizable to other centers. The chart review consisted of ED visits for 6 months (October 1, 2016-March 30, 2017), and different times of the year, including the holiday season, could have played a role in restraint use. We did not examine the time patients spent in restraints or a follow-up of any injuries or complications that may have resulted from being restrained.
Further studies are needed to examine the risk factors that result in patients being physically restrained, particularly in facilities with no available psychiatric services. These findings can be used to develop protocols and training for health care workers in the early identification of at-risk patients with the goal of a lower rate of physical restraint.
Submitted: April 18, 2019; accepted August 14, 2019.
Published online: November 21, 2019.
Potential conflicts of interest: None.
Funding/support: None.
Previous presentation: This work was presented in part at the American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; May 8, 2018; New York, New York ▪ Central Michigan Public Health Summit; May 11, 2018; Mt Pleasant, Michigan ▪ Central Michigan University 3rd Annual Research Symposium; April 11, 2018; Saginaw, Michigan.
REFERENCES
1.Promoting Alternatives to the Use of Seclusion and Restraint—Issue brief #1: A National Strategy to Prevent Seclusion and Restraint in Behavioral Health Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website. https://www.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/trauma_and_violence/seclusion-restraints-1.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
2.Knox DK, Holloman GH Jr. Use and avoidance of seclusion and restraint: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Seclusion and Restraint Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):35-40. PubMed CrossRef
3.APA Task Force on Patient Safety. Patient Safety and Psychiatry: Recommendations to the Board of Trustees of the American Psychiatric Association. American Psychiatric Association website. https://www.psychiatry.org/File%20Library/Psychiatrists/Directories/Library-and-Archive/task-force-reports/tfr2003_PatientSafety.pdf. Accessed October 4, 2019.
4.Cotter VT. Restraint free care in older adults with dementia. Keio J Med. 2005;54(2):80-84. PubMed CrossRef
5.Berzlanovich AM, Schöpfer J, Keil W. Deaths due to physical restraint. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2012;109(3):27-32. PubMed
6.Kalula SZ, Petros SG. Use of physical restraint in hospital patients: a descriptive study in a tertiary hospital in South Africa. Curationis. 2016;39(1):e1-e8. PubMed CrossRef
7.Kr×¼ger C, Mayer H, Haastert B, et al. Use of physical restraints in acute hospitals in Germany: a multi-centre cross-sectional study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50(12):1599-1606. PubMed CrossRef
8.Martin B, Mathisen L. Use of physical restraints in adult critical care: a bicultural study. Am J Crit Care. 2005;14(2):133-142. PubMed
9.Patel A, Chan W, Aparasu RR, et al. Effect of psychopharmacotherapy on body mass index among children and adolescents with bipolar disorders. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(4):349-358. PubMed CrossRef
10.Zun LS. A prospective study of the complication rate of use of patient restraint in the emergency department. J Emerg Med. 2003;24(2):119-124. PubMed CrossRef
11.Carpenter-Song E, Whitley R, Lawson W, et al. Reducing disparities in mental health care: suggestions from the Dartmouth-Howard collaboration. Community Ment Health J. 2011;47(1):1-13. PubMed CrossRef
12.San L, Marksteiner J, Zwanzger P, et al. State of acute agitation at psychiatric emergencies in Europe: The STAGE Study. Clin Pract Epidemol Ment Health. 2016;12(1):75-86. PubMed CrossRef
13.Knutzen M, Sandvik L, Hauff E, et al. Association between patients’ gender, age and immigrant background and use of restraint—a 2-year retrospective study at a department of emergency psychiatry. Nord J Psychiatry. 2007;61(3):201-206. PubMed CrossRef
14.Hadi F, Khosravi T, Shariat SV, et al. Predictors of physical restraint in a psychiatric emergency setting. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015;29(296):296. PubMed
15.Telintelo S, Kuhlman TL, Winget C. A study of the use of restraint in a psychiatric emergency room. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1983;34(2):164-165. PubMed
Please sign in or purchase this PDF for $40.00.
Save
Cite