Objective: To assess the prevalence and associated factors of depression among diabetic outpatients in 2 hospitals in Ethiopia.
Methods: This institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted from April to May 2018. A systematic random-sampling technique was used to select study participants. Depression was assessed with the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Depression. Logistic regression analysis was used, and strength of the association was presented as adjusted odds ratio (AOR) with 95% CI; P
Results: The prevalence of depression among patients with diabetes was 37.8% (95% CI, 33.2%-42.6%). Female sex (AOR = 5.33, 95% CI, 3.05-9.33), type 2 diabetes mellitus (AOR = 3.28, 95% CI, 1.69-6.36), comorbid disease (AOR = 2.84, 95% CI, 1.39-5.83), current substance use (AOR = 1.74, 95% CI, 0.42-7.29), high fear of complications (AOR = 1.76, 95% CI, 1.05-2.93), and poor social support (AOR = 1.94, 95% CI, 1.03-3.67) were significantly associated with depression.
Conclusions: In the current study, the prevalence of depression among diabetic outpatients was higher than that of studies conducted in other settings. Depression was significantly associated with female sex, rural residency, type 2 diabetes mellitus, duration of illness > 6 years, high fear of complications, and poor social support.
ABSTRACT
Objective: To assess the prevalence and associated factors of depression among diabetic outpatients in 2 hospitals in Ethiopia.
Methods: This institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted from April to May 2018. A systematic random-sampling technique was used to select study participants. Depression was assessed with the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Depression. Logistic regression analysis was used, and strength of the association was presented as adjusted odds ratio (AOR) with 95% CI; P <.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: The prevalence of depression among patients with diabetes was 37.8% (95% CI, 33.2%–42.6%). Female sex (AOR = 5.33, 95% CI, 3.05–9.33), type 2 diabetes mellitus (AOR = 3.28, 95% CI, 1.69–6.36), comorbid disease (AOR = 2.84, 95% CI, 1.39–5.83), current substance use (AOR = 1.74, 95% CI, 0.42–7.29), high fear of complications (AOR = 1.76, 95% CI, 1.05–2.93), and poor social support (AOR = 1.94, 95% CI, 1.03–3.67) were significantly associated with depression.
Conclusions: In the current study, the prevalence of depression among diabetic outpatients was higher than that of studies conducted in other settings. Depression was significantly associated with female sex, rural residency, type 2 diabetes mellitus, duration of illness > 6 years, high fear of complications, and poor social support.
Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2020;22(2):19m02479
To cite: Jarso MH, Likasa DD. Prevalence and associated factors of depression among diabetic outpatients in Ethiopia. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19m02479.
To share: https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.19m02479
© Copyright 2020 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
aDepartment of Psychiatry, Faculty of Public Health and Medical Sciences, Mettu University, Mettu, Ethiopia
*Corresponding author: Mohammedamin Hajure Jarso, MH, MSc, Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Public Health and Medical Sciences, Mettu University, postal code 957, Mettu, Ethiopia ([email protected]).
Diabetes mellitus comprises a heterogeneous group of metabolic diseases characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and disturbances in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism resulting from defects in insulin secretion or insulin action. Globally, an estimated 422 million adults are living with diabetes mellitus.1 There is substantial evidence that diabetes is an epidemic in many low- and middle-income countries, with an increasing proportion of affected people in younger age groups.2 In the Global Burden of Disease study,2 diabetes was in 10th place with 2.3% of the overall disease burden as a percentage of the overall disability-adjusted life-years.
Research has shown depression to be associated with high mortality in people with diabetes.3 In addition, depression remains undiagnosed in 50%–75% of diabetes cases.3 In Ethiopia, depression contributes to about 6.5% of the burden of disease, which is the highest share of burden compared to other forms of mental disorders.4 Depression is higher among those with diabetes than in the general population according to a recent study.5
Depression among patients with diabetes may lead to poor treatment adherence, poor treatment outcome, and, consequently, worsened quality of life.6 A bidirectional association exists between depression and diabetes. The presence of diabetes doubles the odds of comorbid depressive disorder.7 A study8 concluded that depression in people with diabetes may lead to poor concordance with medical management, reduced motivation for self-management activity, greater severity of the physical illness, higher mortality, and higher health care costs. However an earlier study9 showed that timely identification of patients with subthreshold or clinical depression with a structured approach for the management of depression in diabetes has proved to be effective in reducing the burden of depression in diabetes.
A cross-sectional study10 conducted in the United States revealed that nearly 18% of diabetic patients had major depression. A study11 conducted in central Romania indicated a prevalence of depression among diabetic patients of 41.7%, and presence of comorbid depression in patients with diabetes was associated with risk for developing dementia. Another cross-sectional study12 of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Lithuania found the prevalence of mild to severe depression was 28.5%. However, a study13 from Pakistan found a more modest depression prevalence (14.7%) among patients with diabetes.
The overall prevalence of depression among diabetes patients in Dare Selam, Tanzania was 87%; 78.8% of those patients had minimal to mild depression, 8.2% had moderate depression, and none had severe depression.13 A study14 in Uganda revealed the prevalence of depression was 34.8%. Little is known regarding data in East Africa; however, 2 studies15,16 conducted in Ethiopia (Bahirdar and Gondar City) revealed the overall prevalence of depression among patients with diabetes was 40.4% and 15.4%, respectively.
A cross-sectional study17 conducted in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia indicated that factors associated with depression in hospitalized diabetic patients were older age, lower educational level, lower income, and job status (retired or unemployed). Most studies indicate the risk of developing depression is higher in patients with diabetes-related complications.18–22 Poor social support has been shown to be significantly associated with depression among diabetic patients in various studies.23–26
METHODS
This institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted from April to May 2018 in Harar City, the capital of Harari national state. Harari national state is located in the eastern part of Ethiopia, which is 526 km from Addis Ababa, and it has a total area of 304.51 km2. In Harar City, there are 2 governmental hospitals, 1 federal police hospital, 1 Army hospital, 2 private general hospitals, and 1 Fistula hospital; 8 government health centers; 1 regional public health laboratory and research center and 1 nursing school; and 19 health posts that provide health care services.
The patients were informed of the study objectives, that depression was the targeted condition, and that no incentives would be given. All patients of Jugol and Hiwot Fana Hospital who met the study criteria before data collection were included. Patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and those who were unable to communicate because of serious illness were excluded. Among 853 patients with diabetes who had regular follow-up at diabetes clinics, 407 patients were recruited for the study. Systematic random sampling was conducted, and participants were approached every second interval. Data were collected by face-to-face interview in Amharic and Afaan Oromo languages using structured questionnaires and chart review.
Instruments
The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Depression (HADS-D)27 is a questionnaire that contains a 7-item subscale for depression. The HADS-D was validated in Ethiopia, with an internal consistency of 0.76 for the depression subscales and 0.87 for the full scale. The scale uses a cutoff score for depression of ≥ 8. The HADS-D was previously translated into Amharic and validated in Ethiopia and has been used for institutional-based study, with a sensitivity and specificity of 0.86 and 0.81, respectively.27
The Fear of Complication Questionnaire28is a 15-item self-assessment instrument designed to measure fear of complications in diabetes mellitus. The reliability (internal consistency) of the questionnaire was measured using Cronbach α and was found to be 0.94 (95% CI, 0.923–0.952).28
The 3-item Oslo Social Support Scale29 was used to assess social support. Raw scores are summarized, with the sum ranging from 3 to 14.
Sexual dysfunction was measured with the Changes in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire,30 which contains separate male and female clinical versions. The instrument has a Cronbach α of 0.91 and 0.93 for the male and female scales, respectively.30
Operational Definitions
The operational definitions were as follows:
Depression (yes/no). Cutoff point ≥ 8 using the HADS-D subscale.
Current substance use. Use of at least 1 specified substance in the past 3 months; ever use was defined as use of at least 1 specified substance during the patient’s lifetime.
Regular physical activity. Exercised for at least 30 minutes or walked for 3 or more days per week.
Social support. Poor support: 3-item score of 3–8, moderate support: score of 9–12, and strong support: score of 12–14 using the 3-item Oslo Social Support Scale.
Glycemic control. Good glycemic control: fasting blood glucose of 70–130 mg/dL; poor glycemic control: fasting blood glucose < 70 mg/dL and > 130 mg/dL.
Fear of diabetes complications. Low fear: mean score ≤ 11; high fear: mean score ≥ 12.
Change in sexual functioning. Male sexual dysfunction defined as score ≤ 49 from total score and female sexual dysfunction defined as score ≤ 43 from total score using the Changes in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire.
Chronic complication of diabetes. Includes microvascular (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy) and macrovascular complications.
Cardiovascular disease. Refers to a class of diseases that involve heart or blood vessels, with the exception of hypertension.
Data Processing and Analysis
Data were checked for completeness and consistency and then coded. Coded variables were entered into EpiData version 3.1 (EpiData Association, Odense, Denmark) and transferred into SPSS version 20.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, New York) for analysis. These data are presented as frequencies, percentages, cross-tabulations, and adjusted odds ratios (AORs). The association between dependent and independent variables was assessed using binary logistic regression. All explanatory variables with a P value ≤ .20 in the bivariate logistic analysis were fitted into multivariate logistic regression to identify independently associated factors in the final model. The strength of the association is presented as AOR with 95% CI, and P < .05 is considered statistically significant.
Ethical Consideration
Ethical clearance was obtained from the ethical board of Gondar University and Amanuel Mental Specialized Hospital, and permission was obtained from concerned stakeholders. Patients provided informed consent to participate in the study.
RESULTS
Sociodemographic Characteristics
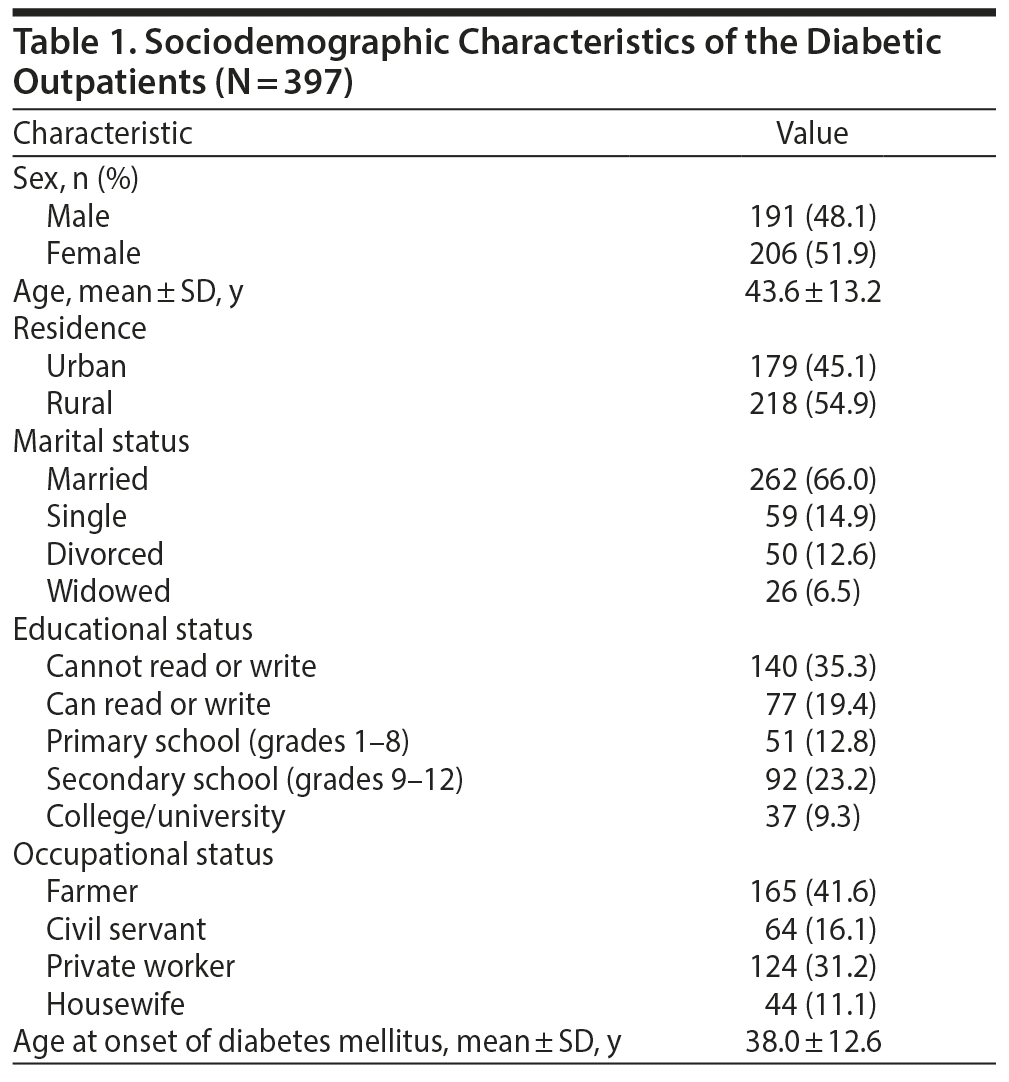
A total of 407 participants were recruited, of whom 397 responded (97.5%).The mean age and age at onset of illness of the study participants were 43.6 ± 13.2 and 38.0 ± 12.6 years, respectively. Of the participants, 262 (66.0%) were married, 206 (51.9%) were women, 140 (35.3%) could not read or write, and only 92 (23.2%) attended secondary school. In addition, more than half of the respondents (n = 218, 55%) lived in an urban area. Table 1 provides the sociodemographic characteristics of the subjects.
Clinical Characteristics of the Study Participants
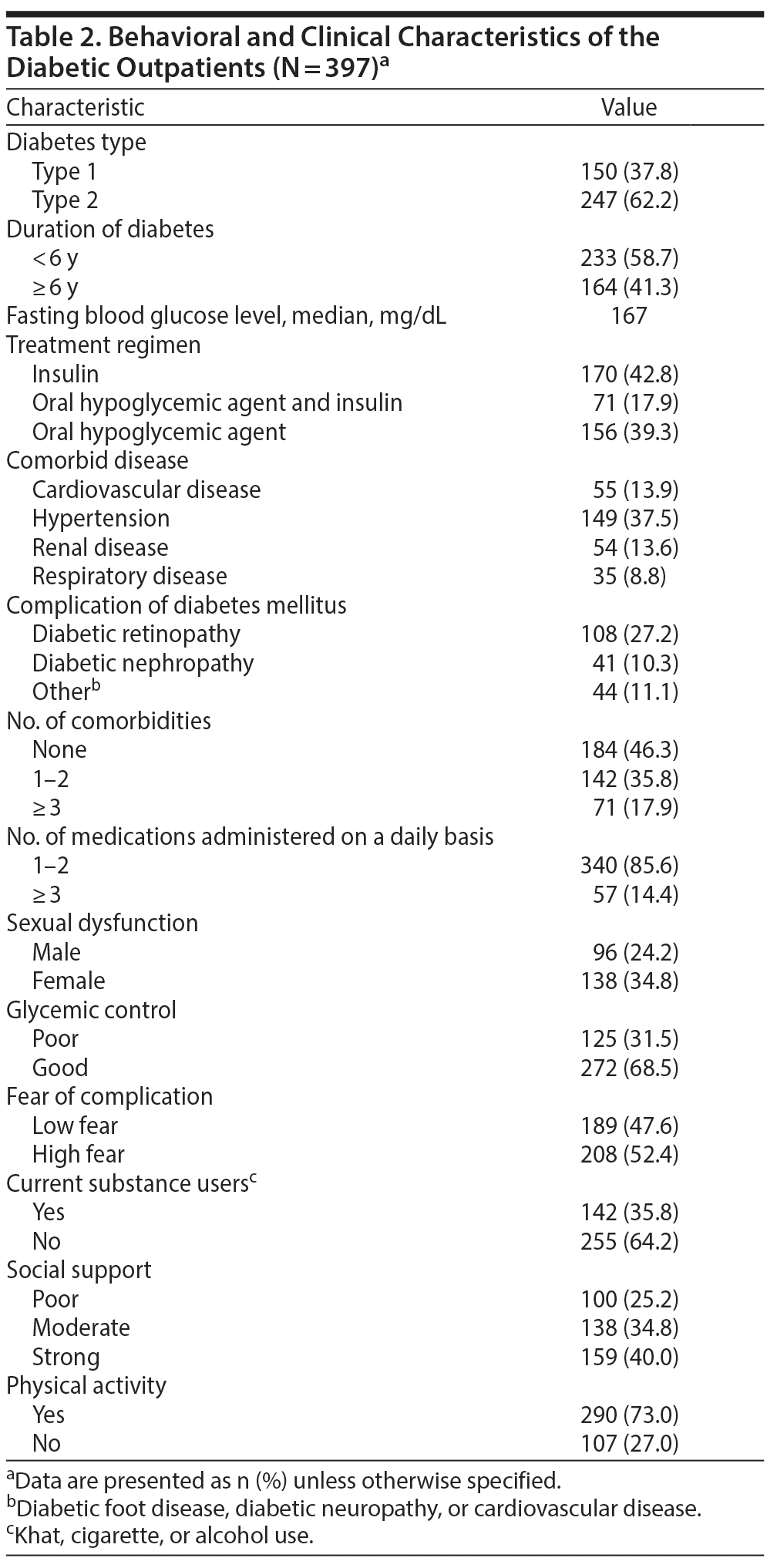
With regard to clinical characteristics of study participants, 150 (37.8%) and 247 (62.2%) patients were found to have type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, and 233 (58.7%) had been receiving diabetes treatment for < 6 years (Table 2). The mean ± SD fasting blood glucose level of study participants was 189.61 ± 96.31 mg/dL. With regard to comorbidity and complications of diabetes mellitus, 149 (37.5%) and 108 (27.2%) of the respondents had respiratory disease and diabetic retinopathy, respectively. Also, 142 (35.8%) and 156 (39.3%) of the respondents had 1 to 2 comorbid diseases and were on oral hypoglycemic agents, respectively.
Substance Use and Psychosocial Characteristics
of the Study Participants
Of the study participants, 208 (52.4%) were fearful of complications of diabetes (see Table 2), including losing eyesight, kidney problems and dialysis, and cardiovascular disease, and were worried about blood sugar. Regarding social support and substance use, 147 (37.0%) had poor social support, 142 (35.8%) were currently using a substance (khat, alcohol, or tobacco), and 231 (58.2%) reported using a substance (khat, alcohol, or tobacco) in their lifetime.
Prevalence of Depression
The prevalence of depression among patients with diabetes mellitus was 37.8% (95% CI, 33.2%–42.6%) when a HADS-D cutoff score ≥ 8 was used.
Factors Associated With Depression Among the Study Participants
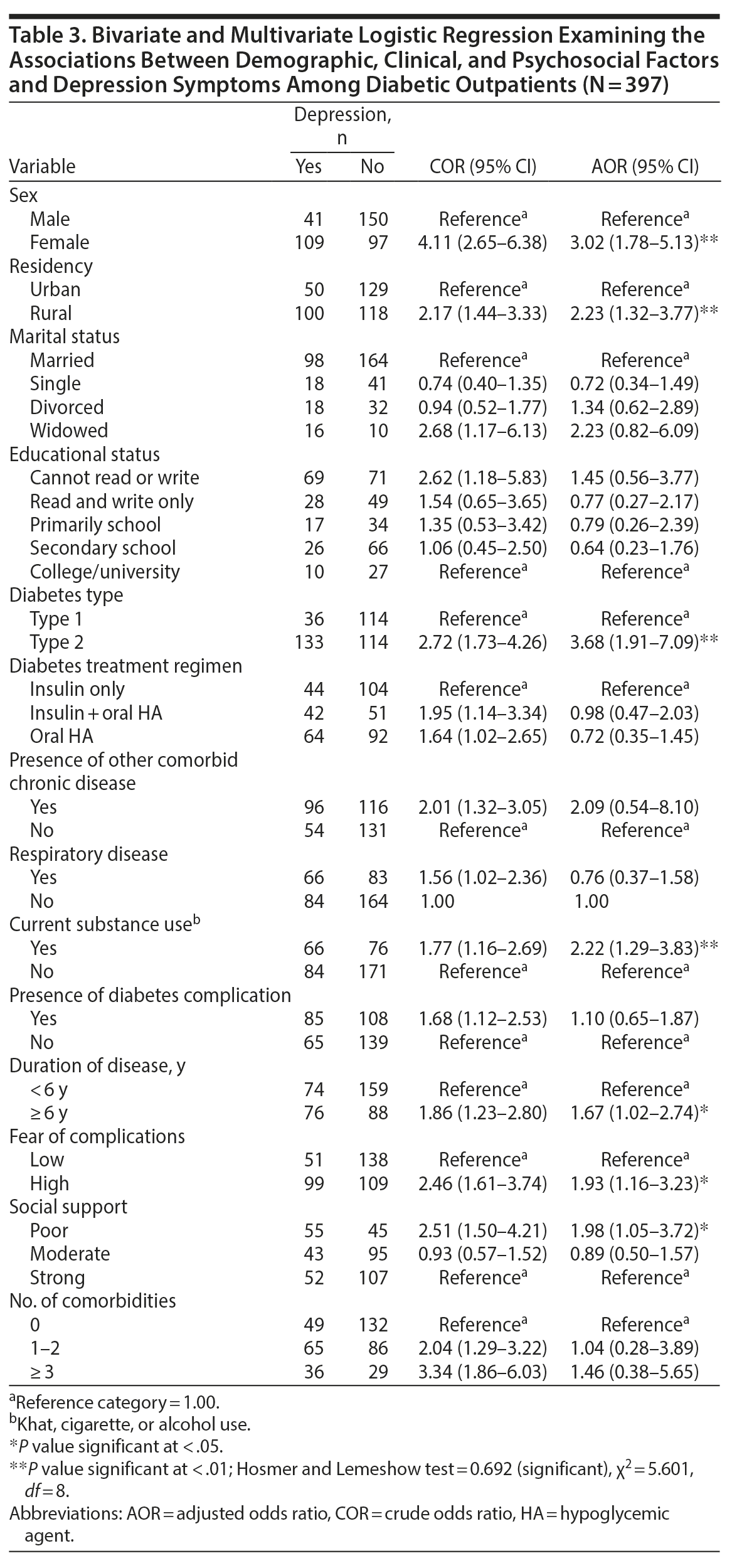
Binary logistic regression analysis revealed that female sex, high fear of diabetes complications, having an additional comorbid diagnosis, having a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus, rural residency, poor social support, having a diabetes mellitus complication, divorced status, current use of a substance, taking insulin and an oral hypoglycemic agent, duration of illness > 6 years, being unable to read or write, having ≥ 3 comorbid diagnoses, and having a comorbid diagnosis of respiratory disease were associated with depression among diabetic patients.
In the multivariate regression model analysis, after controlling for potential confounders, female sex, type 2 diabetes mellitus, rural residency, high fear of complications, duration of illness, current substance use, and poor social support were found to be independent predictors of depression among diabetic patients. The odds of having depression were 3 times higher in female respondents compared to males (AOR = 3.02, 95% CI, 1.78–5.13) (Table 3). Also, rural residents were 2 times more likely to have depression compared to urban dwellers (AOR = 2.23, 95% CI, 1.32–3.77).
Concerning psychosocial factors, the odds of having depression were 2 times higher among those with a high fear of diabetes complications compared to those who were less fearful of complications (AOR = 1.93, 95% CI, 1.16–3.23). Also, individuals with poor social support were 2 times more likely to have depression compared to those who had good social support (AOR = 1.98, 95% CI, 1.05–3.72). With regard to substance use, the odds of developing depression among current substance users were 2 times higher than that of nonusers (AOR = 2.22, 95%, CI, 1.29–3.83). Finally, concerning clinical factors, the odds of having depression were 1.6 times higher among individuals receiving treatment ≥ 6 years compared to those receiving treatment < 6 years. Individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus were 3.7 times more likely to have depression compared to those with a type 1 diagnosis (AOR = 3.68, 95% CI, 1.91–7.09) (see Table 3).
DISCUSSION
The prevalence of depression in this study was 37.8% (95% CI, 33.2%–42.6%). This finding is in line with other studies carried out in Bahirdar, Ethiopia (40.4%)15 and Uganda (34.8%).14 On the other hand, the current study finding is higher than that of studies conducted in the United States,31 Basque,19 Lithuania,12 and Pakistan.32 Possible variations among the studies might include the assessment tool used, having relatively good health care delivery systems, and larger study settings. However, the current study finding was lower than that of similar studies conducted in Iran,33 Tanzania,13 Cameron,21 and the central part of Romania.11 Again, possible variations might be explained by the study design and assessment tool used.
The current study revealed that depression was strongly associated with female sex, type 2 diabetes mellitus, rural residency, > 6 years duration of illness, high fear of complications, current substance use, and poor social support. Female respondents were 3 times more likely to have depression compared to male respondents. A possible reason for this finding could be that women may experience more stress trying to balance work and home life demands including personal relationships, while simultaneously attempting to manage their disease. This finding is in agreement with the results of other published studies from Tanzania,13 Sri-lanka,34 Bangladesh,35 and the United Kingdom.36
In our study, the odds of current substance users developing depression were 2 times higher compared to nonusers. This finding might be due to the association of current substance use with a substantial increase in the complications of diabetes mellitus, particularly those related to the cardiovascular, renal, and neurologic systems, which further increase risk of acquiring depression. The current study finding is supported by studies conducted in Malaysia37 and China.6
In the present study, rural resident patients were 2 times more likely to develop depression compared to urban resident patients. This finding is in contrast to earlier studies conducted in south India.38 A possible reason for this difference might be related to the study setting and psychometric tool used. The earlier study34 data were community based, and the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire was used as a screening tool.
We found that individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were 3 times more likely to have depression compared to individuals with a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. A possible reason could be that the effect of psychological stress counters regulatory hormone activation and biological pathways through which depression might have an impact on diabetes. This finding is similar to those of studies conducted in India,38 Malaysia,37 and the United States31 and at the University of Leicester (United Kingdom).36
The current study found that individuals with > 6 years of illness were 1.67 times more likely to have depressive symptoms compared to those with a lower duration of illness. The possible reason for this finding might be that increased duration of the disease is known to significantly increase the risk of developing diabetes complications and health care expenditures, and, as a result, such patients are more prone to develop psychological illnesses.39 Similarly, this finding is in agreement with studies from Bahrain,40 India,41 and Kenya.42
With regard to psychosocial factors, individuals who felt high fear of diabetes complications were 2 times more likely to have depression compared to those who felt low fear, which is in line with the study conducted in Bahirdar, Ethiopia.15 This increase in depression might result from dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system due to fear of hypoglycemia, complications, or mortality, which are immediate physiologic processes that might prompt higher fear states among the diabetic population.43
Additionally, the odds of having depression were 2 times greater among individuals with poor social support compared to those who had good social support. These results are in line with a previous study17 conducted in Saudi Arabia among diabetic patients. The possible justification for this finding might be that poor social support negatively affects self-care, adherence, and inability to react or deal with stressful situations and may contribute to the development of depression.44
Strengths of the study include use of diagnostic tools with high validity and specificity, which were validated in Ethiopia, and inclusion of different variables such as fear of complications and sexual dysfunction. Despite these strengths, the study has some limitations. First, the cross-sectional nature of the study did not allow us to determine causal relationships between depressive symptoms and poor glycemic control. Second, clinical factors such as diabetes complications included in this study were not confirmed by specialists or by a standardized test but rather were based on chart review and the patient’s subjective response.
Generally, the present findings show a high prevalence of depression, which demands close monitoring and early appropriate management to prevent its progression to more chronic and severe forms.
Clinical Points
- The comorbidity of depression and diabetes is a major health concern.
- Depression and diabetes are significant public health concerns in Ethiopia.
- Depression in diabetes reveals a missed opportunity to reduce the disease burden among diabetic patients.
Submitted: May 11, 2019; accepted September 30, 2019.
Published online: April 2, 2020.
Potential conflicts of interest: None.
Funding/support: This study was supported by Mettu University, Mettu, Ethiopia.
Role of the sponsor: The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of data; or preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Acknowledgement: The authors are grateful to Amanuel Mental Specialized Hospital, University of Gondar, and Mettu University for use of facilities and assistance. The authors also thank Jugol and Hiwot Fana Hospital clinic staff, the data collectors, and the study participants.
REFERENCES
1. Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization website. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/204871/9789241565257_eng.pdf;jsessionid=3A7BB9B7EC90941478C991F5CD23643F?sequence=1. 2016. Accessed March 4, 2020.
2. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization website. https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004update_full.pdf. 2008. Accessed March 4, 2020.
3. Egede LE, Ellis C. Diabetes and depression: global perspectives. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87(3):302–312. PubMed CrossRef
4. Bitew T. Prevalence and risk factors of depression in Ethiopia: a review. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2014;24(2):161–169. PubMed CrossRef
5. Bajwa SJ, Bajwa S, Saroha R. Psychosocial concerns among patients with diabetes attending the preanesthetic and pain clinic. Journal of Social Health and Diabetes. 2018;3(2):72–78. CrossRef
6. Chen YH, Lin HC. Patterns of psychiatric and physical comorbidities associated with panic disorder in a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2011;123(1):55–61. PubMed CrossRef
7. Bruce DG, Davis WA, Hunter ML, et al. Lifetime depression history and depression risk in type 2 diabetes: a case-control study. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(1):38–42. PubMed CrossRef
8. Wilkinson G, Borsey DQ, Leslie P, et al. Psychiatric disorder in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus attending a general hospital clinic: (i) two-stage screening and (ii) detection by physicians. Psychol Med. 1987;17(2):515–517. PubMed CrossRef
9. Katon WJ, Rutter C, Simon G, et al. The association of comorbid depression with mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(11):2668–2672. PubMed CrossRef
10. Katon W. Depression and diabetes: unhealthy bedfellows. Depress Anxiety. 2010;27(4):323–326. PubMed CrossRef
11. Cernea S, Zoltai C, Berbecilă D, et al. Prevalence of depression, anxiety and cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes from the central part of Romania. Acta Med Marisiensis. 2016;62(2):209–216. CrossRef
12. Mikaliūkštienė A, Žagminas K, Juozulynas A, et al. Prevalence and determinants of anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes in Lithuania. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:182–190. PubMed CrossRef
13. Khan ZD. Prevalence of depression and associated factors among diabetic patients in outpatient diabetes clinic. Health Sci J. 2016;8:650–657.
14. Akena D, Kadama P, Ashaba S, et al. The association between depression, quality of life, and the health care expenditure of patients with diabetes mellitus in Uganda. J Affect Disord. 2015;174:7–12. PubMed CrossRef
15. Teshager W, Giorgis B. Prevalence of depression and associated factors among adult diabetic patients attending outpatient department, at Felege Hiwot Referral Hospital, Bahir Dar, Northwest Ethiopia. Int J Heal Sci Res. 2016;6:264–276.
16. Birhanu AM, Alemu FM, Ashenafie TD, et al. Depression in diabetic patients attending university of Gondar Hospital Diabetic Clinic, Northwest Ethiopia. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2016;9:155–162. PubMed
17. El Mahalli AA. Prevalence and predictors of depression among type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2015;9(2):119–126. PubMed
18. Waitzfelder B, Gerzoff RB, Karter AJ, et al. Correlates of depression among people with diabetes: the Translating Research Into Action for Diabetes (TRIAD) study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):215–222. PubMed CrossRef
19. Orueta J. The prevalence of diabetes-related complications and multimorbidity in the population with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Basque Country. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:1059. PubMed
20. Niraula K, Kohrt BA, Flora MS, et al. Prevalence of depression and associated risk factors among persons with type-2 diabetes mellitus without a prior psychiatric history: a cross-sectional study in clinical settings in urban Nepal. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13(1):309. PubMed CrossRef
21. Hall KK, Tambekou J, Penn L, et al. Association between depression, glycaemic control and the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in a diabetic population in Cameroon. S Afr J Psychiatr. 2017;23:983. PubMed
22. Lin EHB, Heckbert SR, Rutter CM, et al. Depression and increased mortality in diabetes: unexpected causes of death. Ann Fam Med. 2009;7(5):414–421. PubMed CrossRef
23. Lopez-de-Andrés A, Jiménez-Trujillo MI, Hernández-Barrera V, et al. Trends in the prevalence of depression in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes in Spain: analysis of hospital discharge data from 2001 to 2011. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0117346. PubMed CrossRef
24. Anderson RJRJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, et al. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(6):1069–1078. PubMed CrossRef
25. Igwe MN, Uwakwe R, Ahanotu CA, et al. Factors associated with depression and suicide among patients with diabetes mellitus and essential hypertension in a Nigerian teaching hospital. Afr Health Sci. 2013;13(1):68–77. PubMed
26. Chew-Graham C, Sartorius N, Cimino LC, et al. Diabetes and depression in general practice: meeting the challenge of managing comorbidity. Br J Gen Pract. 2014;64(625):386–387. PubMed CrossRef
27. Reda AA. Reliability and validity of the Ethiopian version of the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) in HIV infected patients. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):1–6. CrossRef
28. Taylor EP, Crawford JR, Gold AE. Design and development of a scale measuring fear of complications in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2005;21(3):264–270. CrossRef
29. Abiola T, Udofia O, Zakari M. Psychometric properties of the 3-item Oslo Social Support Scale among clinical students of Bayero University Kano, Nigeria. Malaysian J Psychiatry. 2013;22(2).
30. Clayton AH, McGarvey EL, Clavet GJ. The Changes in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire (CSFQ): Development, reliability, and validity. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1997;33(4):731–745.
31. Egede LE, Zheng D, Simpson K. Comorbid depression is associated with increased health care use and expenditures in individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(3):464–470. PubMed CrossRef
32. Zahid N, Asghar S, Claussen B, et al. Depression and diabetes in a rural community in Pakistan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79(1):124–127. PubMed CrossRef
33. Khamseh ME, Baradaran HR, Rajabali H. Depression and diabetes in Iranian patients: a comparative study. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2007;37(1):81–86. PubMed CrossRef
34. Neththasinghe SC. Diabetes and depression: a comparative study of tsunami affected and nonaffected population in Sri Lanka [dissertation]. Oslo, Norway: University of Oslo; 2008.
35. Rahman M, Rahman A, Flora MS. Depression and associated factors in diabetic patients attending an urban hospital of Bangladesh. Int J Collab Res Intern Med Public Health. 2011;3(1):65–76.
36. Ali S, Stone MA, Peters JL, et al. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2006;23(11):1165–1173. PubMed CrossRef
37. Ganasegeran K, Renganathan P, Manaf RA, et al. Factors associated with anxiety and depression among type 2 diabetes outpatients in Malaysia: a descriptive cross-sectional single-centre study. BMJ Open. 2014;4(4):e004794. PubMed CrossRef
38. Rajangam T, Pryashini M, Manickam S. A study of prevalence of depression in type 2 diabetic patients in a tertiary care centre. International J Contemporary Med Res. 2018;5(8):H3–H5.
39. Almeida OP, McCaul K, Hankey GJ, et al. Duration of diabetes and its association with depression in later life: The Health In Men Study (HIMS). Maturitas. 2016;86:3–9. PubMed CrossRef
40. Almawi W, Tamim H, Al-Sayed N, et al. Association of comorbid depression, anxiety, and stress disorders with type 2 diabetes in Bahrain, a country with a very high prevalence of type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest. 2008;31(11):1020–1024. PubMed CrossRef
41. Mathew CS, Dominic M, Isaac R, et al. Prevalence of depression in consecutive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus of 5-year duration and its impact on glycemic control. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012;16(5):764–768. PubMed CrossRef
42. Violet O, Kenn M. Diabetes and clinical research type 2 diabetes mellitus at Kenyatta National Hospital. Kenya Clin Med. 2016;3(1):1–8.
43. de Groot M, Golden SH, Wagner J. Psychological conditions in adults with diabetes. Am Psychol. 2016;71(7):552–562. PubMed CrossRef
44. Ilori HT, Ajetunmobi OA. Cross-sectional study of impact of social support on depression among type 2 diabetics in a secondary health care facility in southwest Nigeria. JAMMR. 2019;29(2):1–8.
Enjoy free PDF downloads as part of your membership!
Save
Cite
Advertisement
GAM ID: sidebar-top